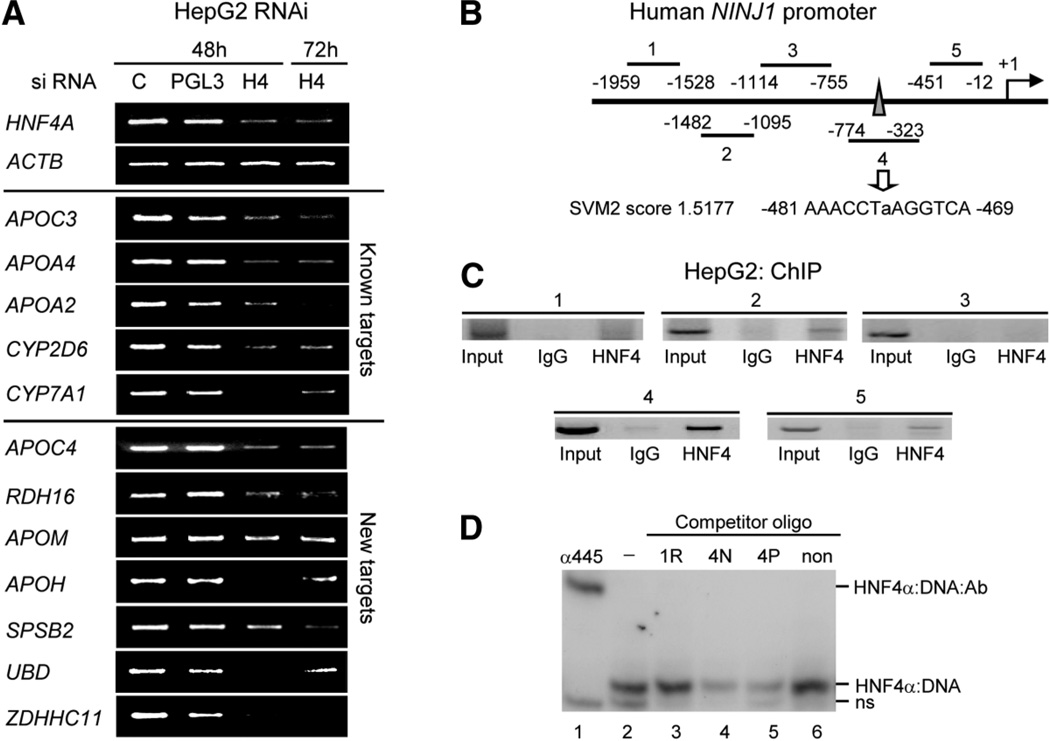
Fig. 5.
HNF4α knockdown in HepG2 cells using RNAi and identification of Ninjurin 1 as a direct target of HNF4α. (A) Verification of HNF4α1/2 knockdown. HepG2 cells treated with siRNA for the hours indicated. Reverse transcription PCR was performed on the indicated HNF4α targets. C, no siRNA. PGL3, control siRNA. H4, HNF4α siRNA (all splice variants from the P1 promoter are targeted). (B) Human NINJ1 promoter showing regions amplified by PCR in ChIP in (C). Region 4 contains a predicted HNF4α-binding site with an SVM2 score of ~1.5177 (moderate binding affinity). (C) ChIP result of HNF4α in HepG2 cells on the human NINJ1 promoter using PCR primers that amplify regions 1–4 noted in (B). IgG, normal rabbit immunoglobulin G; HNF4, α445 antibody. (D) Gel shift assay using nuclear extracts from COS-7 cells transfected with rat HNF4α2, radiolabeled probe from the ApoA1 promoter and unlabeled competitors in 250-fold molar excess corresponding to the SVM site identified in region 4 with native flanking sequences (4N) or PBM flanking sequences (4P) as well as a known nonbinder (non, 175 TTR) and a randomly chosen sequence from region 1 (1R). Shown are the HNF4α:DNA shift complex, a supershift complex with the α445 antibody (HNF4α:DNA:antibody) and nonspecific band from the COS-7 extracts (ns); free probe is not shown. See Supporting Materials and Methods for details on gel shift conditions, Supporting Fig. 5 for immunoblot of HNF4α protein in the RNAi, Supporting Table 3A for a complete list of genes that are down-regulated, Supporting Table 3B for primer sequences, and Supporting Table 8 for gel shift sequences.