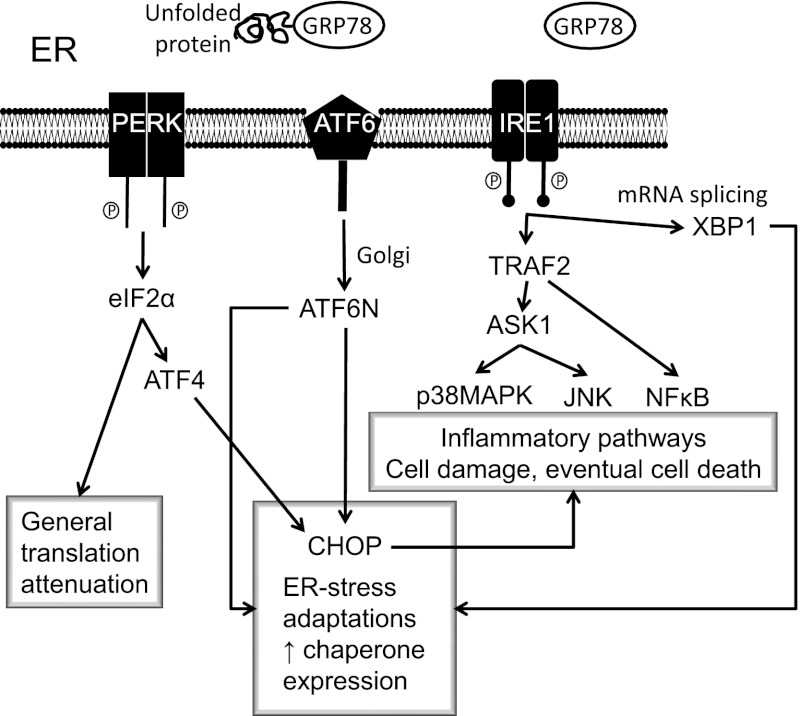
FIG. 1.
ER stress and the unfolded protein response. When ER function is stressed, for example by impaired Ca2+ homeostasis or accumulation of poorly folded proteins, this causes the UPR. The initial response attempts to restore normal function by halting protein synthesis and increasing chaperone production. ER stress also causes activation of proinflammatory pathways, and if prolonged this can lead to cell damage and apoptotic cell death. ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; CHOP, CAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein; eIF2α, eukaryotic translation initiation factor; GRP78, glucose-regulated protein 78; IRE1, inositol-requiring enzyme 1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PERK, PKR-like eukaryotic initiation factor 2A kinase; TRAF2, tumor necrosis factor receptor–associated factor family protein 2; XBP1, X box-binding protein 1.