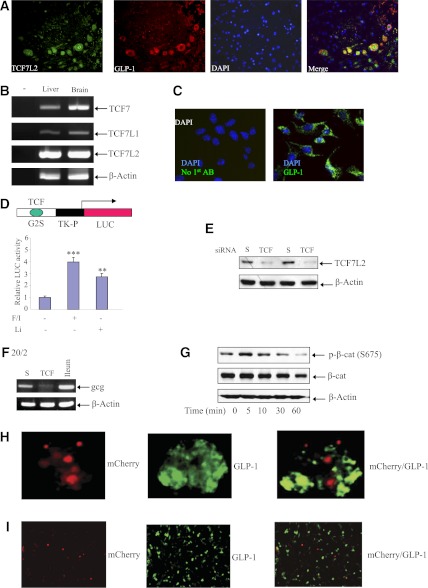
FIG. 3.
TCF7L2 controls gcg expression in the mouse neuronal cell line mHypoE-20/2. A: Immunostaining shows the coexpression of TCF7L2 and GLP-1 in the brainstem of an 8-week-old male FVB mouse. B: RT-PCR shows the detection of TCF7, TCF7L1, and TCF7L2 mRNAs in the mouse brain (liver tissue is a control; primer sequences are shown in Table 1). C: Immunostaining shows GLP-1 expression in the mouse brain mHypoE-20/2 cell line (20/2). D: G2S-LUC expression was stimulated by 4-h lithium (Li; 10 mmol/L) or forskolin and IBMX (F/I; 10 μmol/L each) treatment in mHypoE-20/2 cells. E: Western blotting shows that TCF7L2 siRNA (TCF) but not the scrambled siRNA (S) blocked TCF7L2 expression in mHypoE-20/2 cells (nucleotide sequences of the siRNA are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5). F: Knockdown of TCF7L2 led to a reduced gcg mRNA level (representative RT-PCR result). A mouse distal Ileum (ileum) sample serves as the control for RT-PCR. G: Forskolin and IBMX (10 μmol/L each) treatment shows a temporary stimulation of β-cat S675 phosphorylation in the mHypoE-20/2 cell line. Expressing TCF7L2DN (tagged with mCherry, red) blocked GLP-1 production in gut GLUTag (H) and brain mHypoE-20/2 (20/2) (I) cell lines. The two cells lines were transfected with TCF7L2DN and Tet3G for 24 h, followed by doxycycline (5 ng/mL) treatment for another 24 h. Immunostaining shows that cells express TCF7L2DN (red) do not express GLP-1 (green). **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. (A high-quality digital representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)