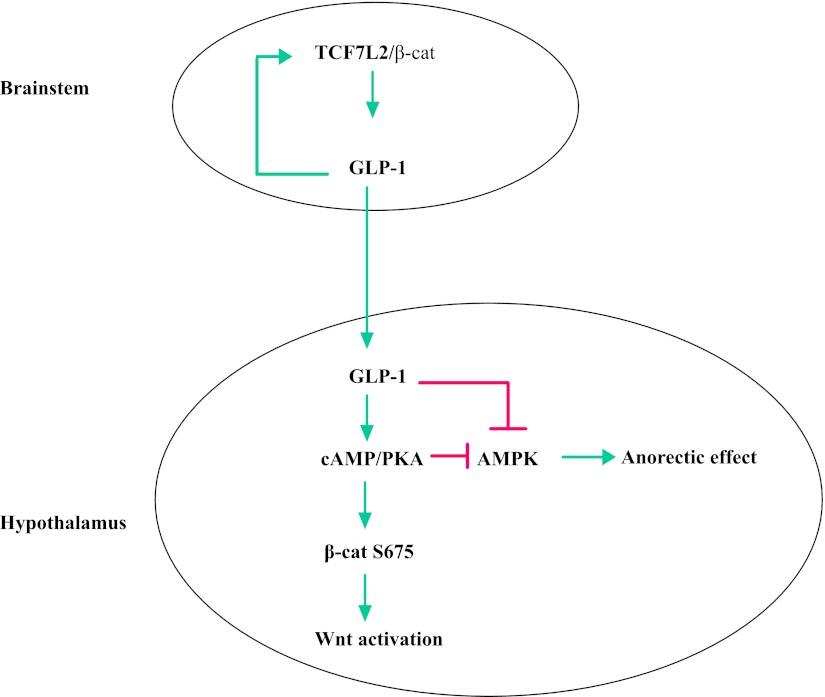
FIG. 7.
A diagram shows the existence of positive feedback between the Wnt and GLP-1/cAMP signaling pathways in the brainstem and hypothalamus. In the brainstem, β-cat/TCF7L2 positively regulates gcg expression and the production of GLP-1, which inhibits food intake at least partially by attenuating hypothalamic AMPK activity (26). GLP-1 also stimulates brain Wnt activity via increasing β-cat Ser675 phosphorylation and, possibly, TCF7L2 production. In the brainstem, this leads to increased gcg expression (positive feedback), whereas in hypothalamic neurons this is among the anorectic effects of GLP-1. How the hypothalamic Wnt activation modulates peripheral glucose homeostasis and insulin signaling is currently unknown. (A high-quality color representation of this figure is available in the online issue.)