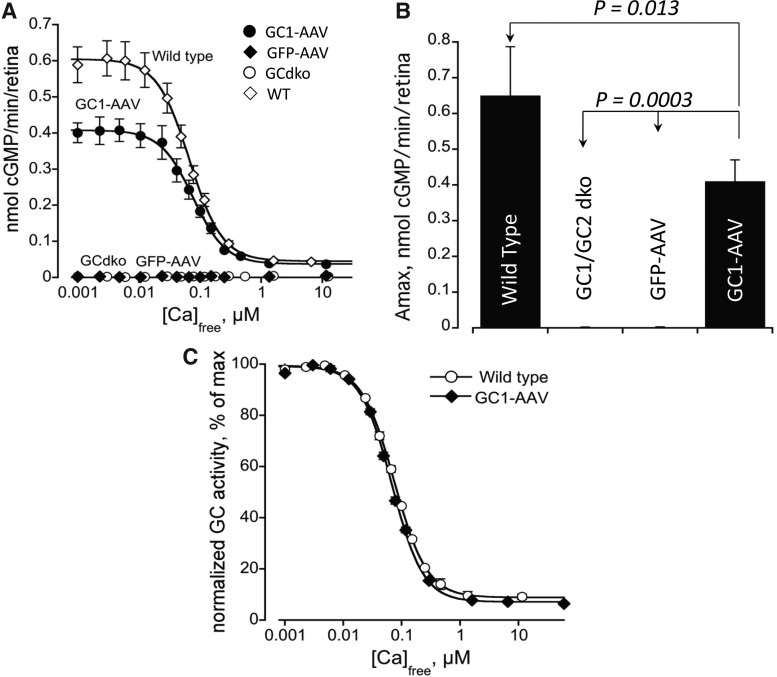
FIG. 5.
Functional efficiency of AAV-mediated RetGC1 activity in vivo. (A) RetGC activity in AAV-GC1–treated GCdko mice (closed circles), control vector AAV-GFP-treated GCdko mice (closed diamonds), age matched GCdko (open circles), and WT (open diamonds) controls at different free Ca2+. Values are the average of three measurements, mean±SE. In both AAV-GFP treated and untreated GCdko mice, the activity was undetectable. (B) Maximal activity of RetGC (at [Ca2+] free<20 nM). On the average, AAV-GC1 restored ∼63% of WT RetGC activity (0.41±0.06 SD, N=3; vs. 0.65±0.137 SD nmol cGMP/min/retina, N=8, respectively). ANOVA/Bonferroni data processing at 99% CL. (C) Ca2+ sensitivity of RetGC in AAV-GC1-treated GCdko mice remains the same as in WT retinas. RetGC activity was normalized by the maximal activity in each series and then averaged from all series for each genotype. The data are fitted by the Hill function, a=(amax − amin)/(1+([Ca]f/Ca1/2)h)+amin; the Ca1/2=68 nM±6 SD, N=8 (wild type) and 74 nM±6 SD, N=3 (GC1-AAV), not a significant difference by t-test (p=0.18); h=1.6±0.056 (WT) and 1.52±0.053 (GC1AAV), not a significant difference by t-test (p=0.1).