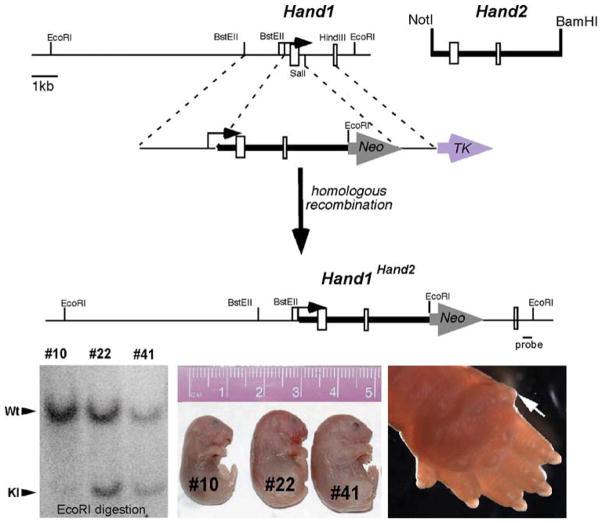
Fig. 1.
Analysis of Hand1Hand2 chimeric mice. (upper panel). The schematic depicts the targeting strategy used. A Hand2 genomic NotI-BamHI fragment containing both exons and lacking the transcriptional start site was cloned downstream of the Hand1 transcriptional start site contained in the Hand1 5′ targeting arm. An additional EcoRI site creates an RFLP, enabling detection of a 3.9-kb EcoRI fragment when a 3′ external probe (indicated) is used (lower right panel). Southern analysis demonstrates chimerism via comparison of the molar ratio of the wild-type (Wt) and knock-in (KI) mutant bands in three newborn F0 age-matched mutant littermate chimeras. Chimera #10 contains less than 15% chimerism control (#10) whereas chimeras #22 and #41 show greater than 95% chimerism (lower middle panel). Stillborn high-percentage Hand1Hand2 (Hd1Hd2) chimeras (#22 and #41) exhibit wholesale edema compared with viable low-percentage unaffected littermates (#10) (lower left panel). Closer examination shows polydactyly in high-percentage Hd1Hd2 chimeras (ectopic posterior digit indicated by the white arrow)