Fig. 3.
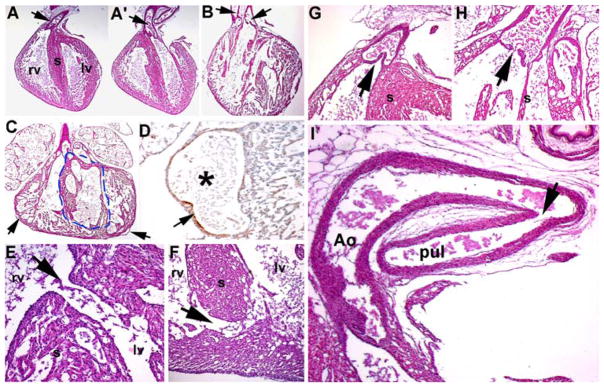
Histologic examination of cardiovascular defects in Hand1Hand2 newborns. a, a′ Wild-type heart depicting the exit of the pulmonary trunk from the right ventricle (arrow in a) and exit of the aorta from the left ventricle (arrow in a′). b Stillborn high-percentage Hd1Hd2 chimeric heart exhibiting double-outlet right ventricle (DORV) as both outflow tract (OFT) vessels exit the right ventricle (arrows), as well as mild hypoplasia of the ventricles, thin myocardial walls, and abnormal perforated septum resulting in both membranous and muscular interventricular septal defects (VSDs). c, d Additional example of high-percentage Hd1Hd2 chimeric heart illustrating ventricular septal hypoplasia (indicated via the dotted line) and dilated coronaries (arrows in c). High-power view of fluid-filled mutant coronary artery (asterisk in d) and incomplete α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA) expression in the supporting muscle layer of the dilated coronaries (arrow in d). e, f Histologic sectioning showing associated perimembranous VSDs (high-percentage chimera shown in panel b) and muscular VSDs (low-percentage chimera). g, h Hd1Hd2 chimeric valve leaflets are hypoplastic and misshapen (chimera in panel b) compared with wild-type littermates. i Stillborn high-percentage Hd1Hd2 chimeras (n = 6) all exhibiting patent ductus arteriosus as the ductus remains open (arrow in i) between the descending aorta (Ao) and the pulmonary trunk (pul), resulting in a high-volume burden on the neonatal lungs and respiratory failure. rv right ventricle, lv left ventricle
