Fig. 5.
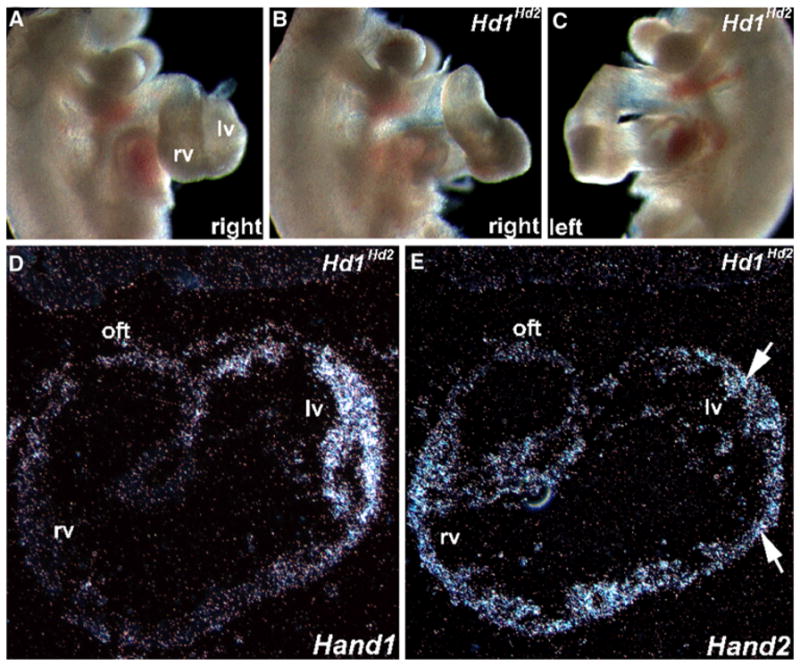
In utero analysis of E10.5 high-percentage Hand1Hand2 chimeric embryos. a–c Whole-embryo right-sided view of a normal E10.5 (a) and both right- (b) and left- (c) sided views of age-matched littermate F0 Hd1Hd2 high-percentage chimeric embryos. Note that the chimeric heart is “unlooped” and farther away from the body of the normal littermate (i.e., both inflow and outflow tract [OFT] are elongated). Otherwise, the chimeric embryos are comparable in size, shape, and structure with their nonchimeric littermates. Also, the chimeric hearts beat at rates comparable with that of control siblings. d, e Using S35 in situ hybridization analysis, sections of the chimeric embryo heart (shown in b and c) were probed with Hand1 (d) and Hand2 (e) cDNA probes. Note that Hand1 mRNA is appropriately expressed in the left ventricle but that Hand2 mRNA is both appropriately expressed in the right ventricle and ectopically expressed in the left ventricle (arrows in e). rv right ventricle, lv left ventricle, oft outflow tract
