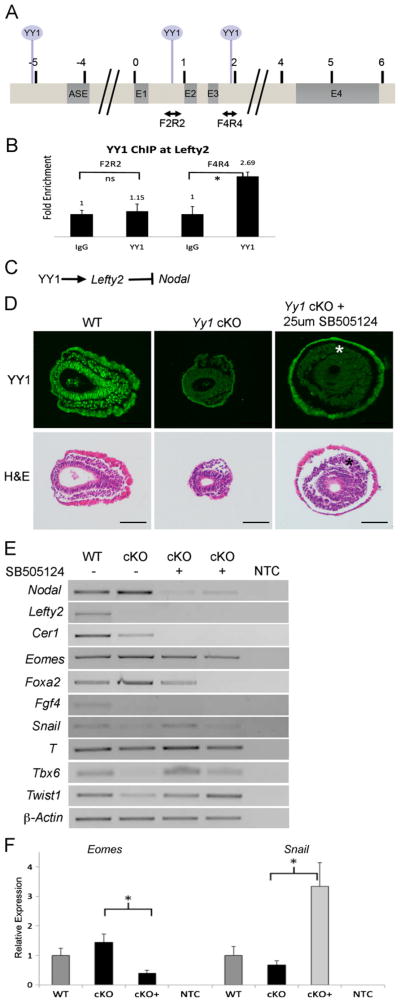
Fig. 5.
YY1 regulates Nodal indirectly through Lefty2. (A) Map of the Lefty2 locus. Double-headed arrows indicate amplicons used for YY1 ChIP and circles above mark locations of predicted YY1 binding sites. (B) YY1 ChIP-qPCR shows that YY1 binds between exons 3 and 4 (F4R4) in vivo, but not between exons 1 and 2. (C) Schematic illustration of possible regulation of Nodal through activation of Lefty2. (D) Transverse sections of untreated wildtype and mutant embryos, as well as mutant embryos cultured with the TGFβ inhibitor SB505124 (top row is YY1 immunofluorescence and bottom row is H and E of the same sections). Treatment with SB505124 results in increased mesodermal-like streak derivatives in mutant embryos (asterisks). (E) RT-PCR indicates that mesodermal markers Tbx6, Twist1 and Snail are increased in the mutants treated with the inhibitor while Lefty2 and Fgf4 expression are unaffected as predicted. RT-PCR also confirms reduction of Nodal, Cer1, Eomes and Foxa2 by treatment with SB505124. F. RT-qPCR confirmation of reduced Eomes and enhanced Snail expression in mutant embryos treated with SB505124. Asterisks represent P values less than 0.05 by student's T-Test. Error bars represent SEM. Scale bars represent 75 μm.