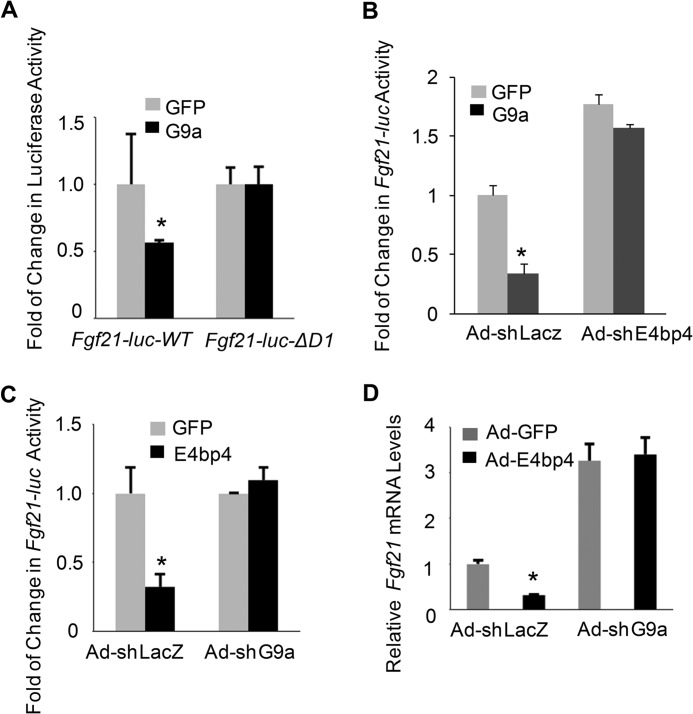
FIGURE 5.
E4BP4 represses Fgf21 expression and promoter activity via G9a. A, G9a repression of Fgf21 requires a functional E4BP4-binding site. Hepa1 cells were transfected with either Fgf21-luc-WT or Fgf21-luc-ΔD1 mutant (D-box 1 deletion) along with G9a expression vector. 48 h later, cells were harvested for the luciferase assay and the β-gal assay as a transfection efficiency control. Data were plotted as mean ± S.E. (error bars) (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 by Student's t test. B, knockdown of E4bp4 abrogates G9a-dependent suppression of the Fgf21 promoter activity in hepatocytes. Hepa1 cells were cotransfected with Fgf21-WT-luc and G9a expression vectors after transduction by either Ad-shLacz or Ad-shE4bp4. 48 h later, cells were harvested for the luciferase assay and the β-gal assay as a transfection efficiency control. Data were plotted as mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 by Student's t test. C, knockdown of G9a abrogates E4BP4-dependent suppression of Fgf21 promoter activity in hepatocytes. Hepa1 cells were cotransfected with Fgf21-WT-luc and E4bp4 expression vector after transduction of either Ad-shLacz or Ad-shG9a. 48 h later, cells were harvested for the luciferase assay and the β-gal assay as a transfection efficiency control. Data were plotted as mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 by Student's t test. D, depletion of G9a blocks E4BP4-dependent repression of Fgf21 mRNA expression in hepatocytes. Hepa1 cells were transduced with the following paired adenoviruses: Ad-GFP plus Ad-shLacz versus Ad-E4bp4 plus Ad-shLacz; Ad-GFP plus Ad-shG9a versus Ad-E4bp4 plus Ad-shG9a. Cells were then synchronized by serum shock and harvested 36 h postsynchronization. Data were plotted as mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.05 by Student's t test.