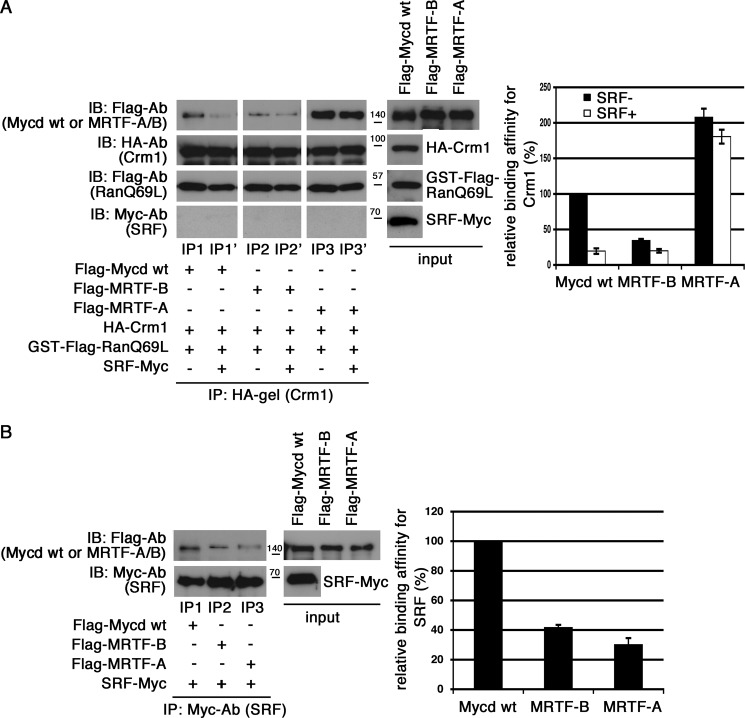
FIGURE 7.
Effects of SRF on interactions between CRM1 and Mycd family members. A, the binding affinities of Mycd family members for CRM1 and the inhibitory effects of SRF on their interactions were compared. Mixtures of HA-tagged CRM1, GTP-bound GST-FLAG-RanQ69L, and each of the indicated FLAG-tagged Mycd family members with or without Myc-tagged SRF were subjected to IP analyses as described in the legend for Fig. 1 (left). The respective IP/IB signal intensities were quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The percentages indicate relative binding affinities for CRM1 normalized by the affinity of Mycd WT in the absence of SRF, which was set at 100% (right). Results are means ± S.E. of three independent experiments (error bars). The reductions in binding affinities for CRM1 by SRF were calculated as follows: 19.5 ± 3.9% for Mycd WT, 57.4 ± 5.0% for MRTF-B, and 88.1 ± 1.5% for MRTF-A. Each of the binding affinities in the absence of SRF was set at 100%. B, differences in the binding affinities of Mycd family members for SRF. Mixtures of Myc-tagged SRF and each of the indicated FLAG-tagged Mycd family members were immunoprecipitated with anti-Myc antibody and protein A-Sepharose. The immunoprecipitates thus obtained were analyzed by IB using the indicated antibodies (left). In control experiments using a control antibody, no significant signals were observed on immunoblots (data not shown). The respective IP/IB signal intensities were quantified as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The percentages indicate relative binding affinities for SRF normalized by the affinity of Mycd WT, which was set at 100% (right). Results are means ± S.E. of three independent experiments (error bars).