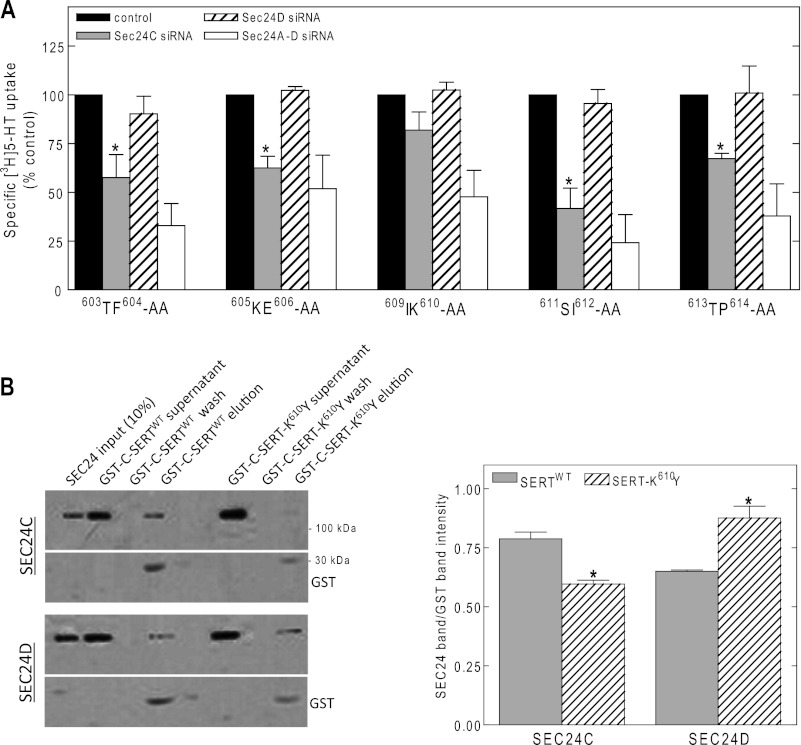
FIGURE 2.
SEC24 requirement of alanine scanning mutants in the region flanking the 607RI608 motif of SERT (A) and pulldown of SEC24C by GST fusion proteins comprising the C terminus of wild type SERT or the K610Y mutant thereof (B). A, HeLa cells were transfected with siRNAs directed against SEC24 isoforms and plasmids encoding the indicated SERT mutants, which scan the region spanning from Thr603 to Pro614. Specific [3H]5-HT uptake (n = 3–4, performed in triplicates; error bars indicate S.E.) was measured to assess the impact of depleting either SEC24C, SEC24D, or all four SEC24 isoforms on cell surface expression of the mutated versions of SERT. The data are expressed as percentages of control for each of the mutants; mean control uptake values were: T603A,F604A (603TF604-AA), 17 ± 4 pmol/106 cells/min; K605A,E606A 605KE606-AA), 20 ± 6 pmol/106 cells/min; I609A,K610A (609IK610-AA), 20 ± 3 pmol/106 cells/min; S611A,I612A (611SI612-AA), 24 ± 5 pmol/106 cells/min; and T613A,P614A (613TP614-AA), 21 ± 4 pmol/106 cells/min. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.05, t test for paired data) between down-regulation of SEC24C (gray bars) and SEC24D (hatched bars). The combined knockdown of all four SEC24 isoforms (white bar) differed in a statistically significant manner from control (full bar) (p < 0.01). B, GST pulldown experiments were performed as described under “Experimental Procedures” with purified fusion proteins comprising the C terminus of wild type SERT (GST-C-SERT) or of SERT-K610Y (GST-C-SERT-K610Y). The bands illustrate that wild type GST-C-SERT interacts with SEC24C to a visibly larger extent than the GST-C-SERT-K610Y mutant. Shown is the input (10%) and volume corrected aliquots of the supernatant, the last wash, and the eluate. The experiment was reproduced twice with similar results. The data were quantified (expressed as ratio of SEC24C/GST versus SEC24D/GST integrated band intensity), and the mutant was compared with the wild type SERT as shown in the rightmost bar diagram. *, significantly different (p < 0.05, t test) with respect to the wild type transporter.