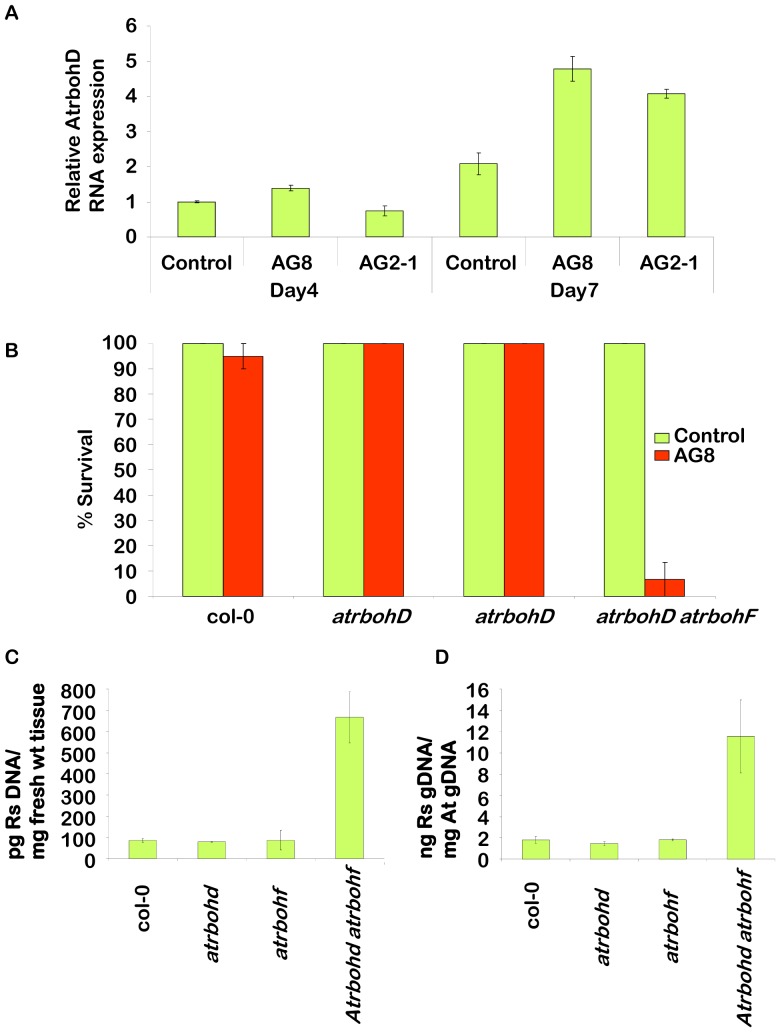
Figure 4. Analysis of the role of NADPH oxidases in resistance to R. solani AG8.
A. Real time PCR of the genes, AtrbohD and AtrbohF. Three biological replicates and two technical repeats were analysed at each time point (four and seven day after infecting one week old seedlings) and treatment (non-infected control, AG8 and AG2-1). The average of each time point and treatment is presented with standard error bars. Cyclophilin was used as the reference gene. Day four (control) is standardized to equal one and all other treatments and time points reflect their fold induction compared to this point. A star above the bar is indicated if the value is significantly different from the control (Dunnett's test p<0.05). B. Survivorship of homozygous atrbohD (SALK_005853C – At5g47910), homozygous atrbohF (SALK_034674C – At1g64060), the double knockout atrbohD atrbohF (CS9558 - At5g47910 & At1g64060) and Col-0 in response to R. solani AG8 compared to WT. Seedling survivorship was recorded two weeks after planting seedlings into pre-infected pots. C. Relative R. solani genomic DNA in homozygous atrbohD, homozygous atrbohF, the double knockout atrbohD atrbohD and Col-0 in response to R. solani AG8 compared to WT at nine days after infection. Quantification of R. solani is presented as ng fungal DNA/µg plant DNA and D. ng fungal DNA per mg of infected tissue used for DNA extraction.