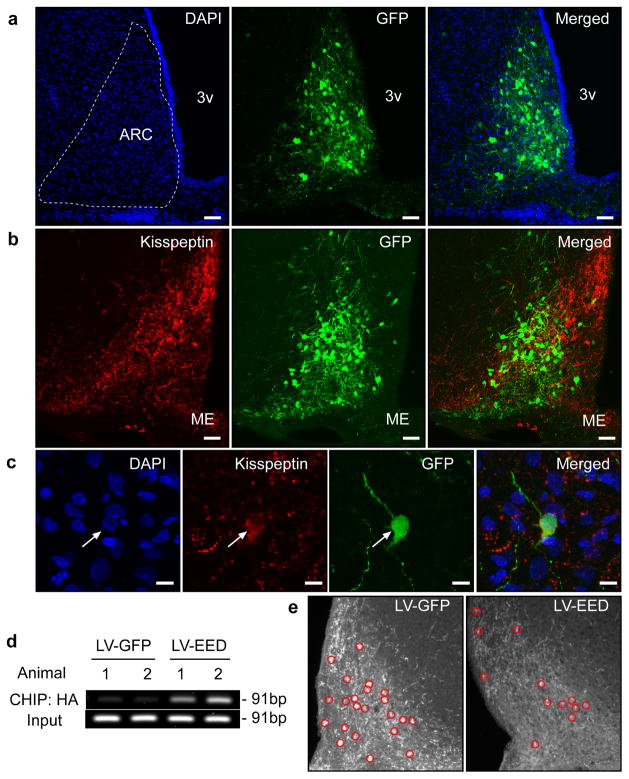
Figure 6. EED delivered to the ARC of immature female rats is recruited to the Kiss1 promoter and represses kisspeptin expression.
Double immunostaining for GFP (Green) and Kisspeptin (Red) in the ARC of an LV-EED injected 44 day-old rat. (a) Cell nuclei of the ARC region identified by DAPI staining (blue) and transduction of ARC neurons by the LV-EED construct. (b) Kisspeptin positive neurons transduced by LV-EED. (c) Higher magnification view of a kisspeptin neuron transduced with the LV-EED construct. Scale bars: 100μm (a–b), 10μm (c). (d) CHIP assay from two controls (LV-GFP) and two experimental (LV-EED) animals showing association of EED-HA to a genomic region that includes the Kiss1 transcription start site as determined by PCR amplification of DNA immunoprecipitated with antibodies recognizing the HA epitope tagging EED. (e) Detection of kisspeptin neuron cell bodies in the ARC after micro-injection of either LV-GFP or LV-EED. Red circles identify kisspeptin positive cell bodies.