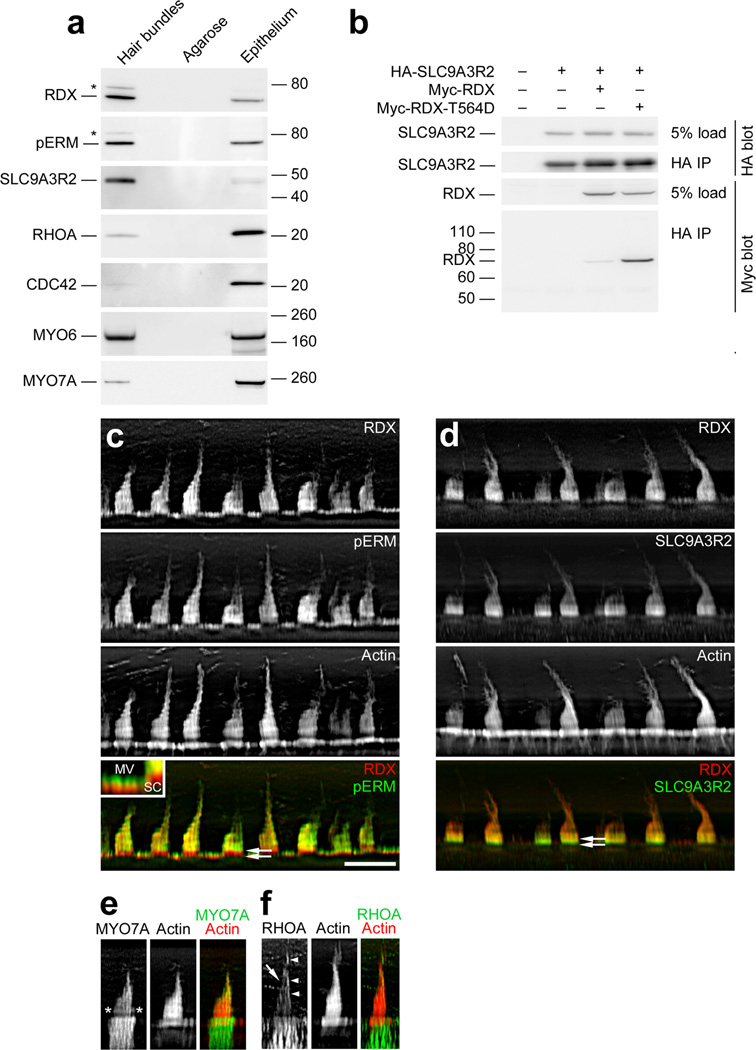
Figure 5.
Identification of RDX and SLC9A3R2 in hair bundles. (a) Protein immunoblotting with purified hair bundles. Lanes from left to right for each blot: Hair bundles, bundles from 40 chick ears (~0.6 µg total protein); Agarose, agarose equivalent to that in the bundles sample; Epithelium, utricle sensory epithelium from 4 chick ears (~10 µg protein). Antibodies used are indicated at left. Both anti-RDX and anti-pERM (which recognizes phosphorylated ezrin, radixin, and moesin) detected bands both at the expected size (~70 kD) and at ~80 kD (asterisk). (b) RDX-SLC9A3R2 interaction. Epitope-tagged chick WT RDX, T564D-RDX, and SLC9A3R2 were expressed in HEK cells in the indicated combinations. Tagged SLC9A3R2 was immunoprecipitated, and associated RDX was detected by immunoblotting. (c) RDX and pERM immunocytochemistry. RDX and pERM co-localize except in the taper region (double arrows in bottom panel). Inset, magnification of apical surfaces of supporting and hair cells. Note that pERM immunoreactivity is absent from bases of microvilli (MV), as in stereocilia (SC). Scale bar in panel c is 10 µm and applies to panels c-f. (d) RDX and SLC9A3R2 immunocytochemistry. RDX and SLC9A3R2 overlap throughout the bundle, but SLC9A3R2 is more concentrated towards stereociliary bases (double arrows in bottom panel), including the tapers, than is RDX. (e) MYO7A immunocytochemistry. MYO7A is concentrated towards stereociliary tips and in a band above the taper region (asterisks). (f) RHOA immunocytochemistry. Staining is seen in stereocilia (arrow) and the kinocilium or the tallest stereocilia of the bundle (arrowheads). RHOA is also substantially enriched in hair cells over supporting cells.