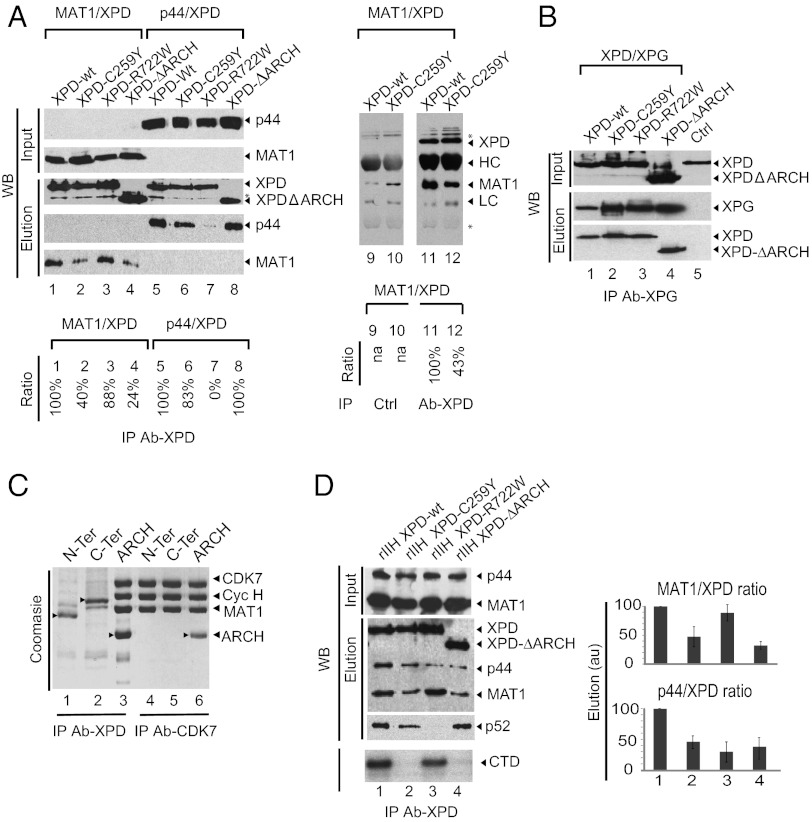
Fig. 4.
The ARCH domain is a recruitment platform for CAK. (A) Pairwise interactions between XPD variants and MAT1 or p44. Sf9 insect cells were coinfected with viruses that allow the expression of Flag-tagged XPD variants and a virus that allows the expression of MAT1 or p44. Proteins were immunopurified with the anti-Flag M2 resin (Left) or were immunoprecipitated with an anti-XPD antibody (Right) in the presence of 250 mM NaCl (buffer C). Input and purified complexes were analyzed by anti-p44, anti-MAT1, or anti-Flag Western blot. The asterisk indicates a nonspecific band. (B) Pairwise interactions between XPD variants and XPG. Sf9 insect cells were coinfected with viruses that allow the expression of Flag-tagged XPD variants and a virus that allows the expression of c-myc–tagged XPG. Immunopurification was performed with anti–c-Myc resin in buffer C. Input and the purified complexes were analyzed by Western blot with anti-Flag antibody. (C) Interactions between XPD fragments and CAK. Sf9 insect cells were coinfected with a virus that allows the expression of the CAK subcomplex with CDK7 C-terminal Strep-tag fusion and with viruses that allow the expression of N-terminal XPD (residues 1–245), C-terminal XPD (residues 443–762), or ARCH (residues 245–443) with an N-terminal Flag tag. The capacity of XPD fragments to bind CAK and to copurify was tested using the Flag-tag (lanes 1–3) or Strep-tag II (lanes 4–6) for the purification of the complexes in buffer C. Purified proteins were analyzed using PAGE with 12% (wt/vol) polyacrylamide followed by Coomassie staining. Proteins are indicated by arrowheads. (D) Consequences of XPD mutations on association with CAK and core-TFIIH. Insect cells were infected with a set of baculoviruses overexpressing the subunits of TFIIH including either wild-type or mutated Flag-tagged XPD, and complexes were immunoprecipitated using an antibody directed toward the Flag epitope in buffer C. After elution with the Flag synthetic peptide, immunopurified complexes (rIIHs) were analyzed by Western blot analysis (WB, Upper) and were tested for their capacity to phosphorylate the CTD of RNA Pol II (autoradio, Lower). Experiments were performed in triplicate. Histograms represent estimated ratios (in arbitrary units, au) between MAT1 (a representative CAK subunit) and XPD or p44 (a representative core-TFIIH subunit).