Figure 1. mTOR signaling.
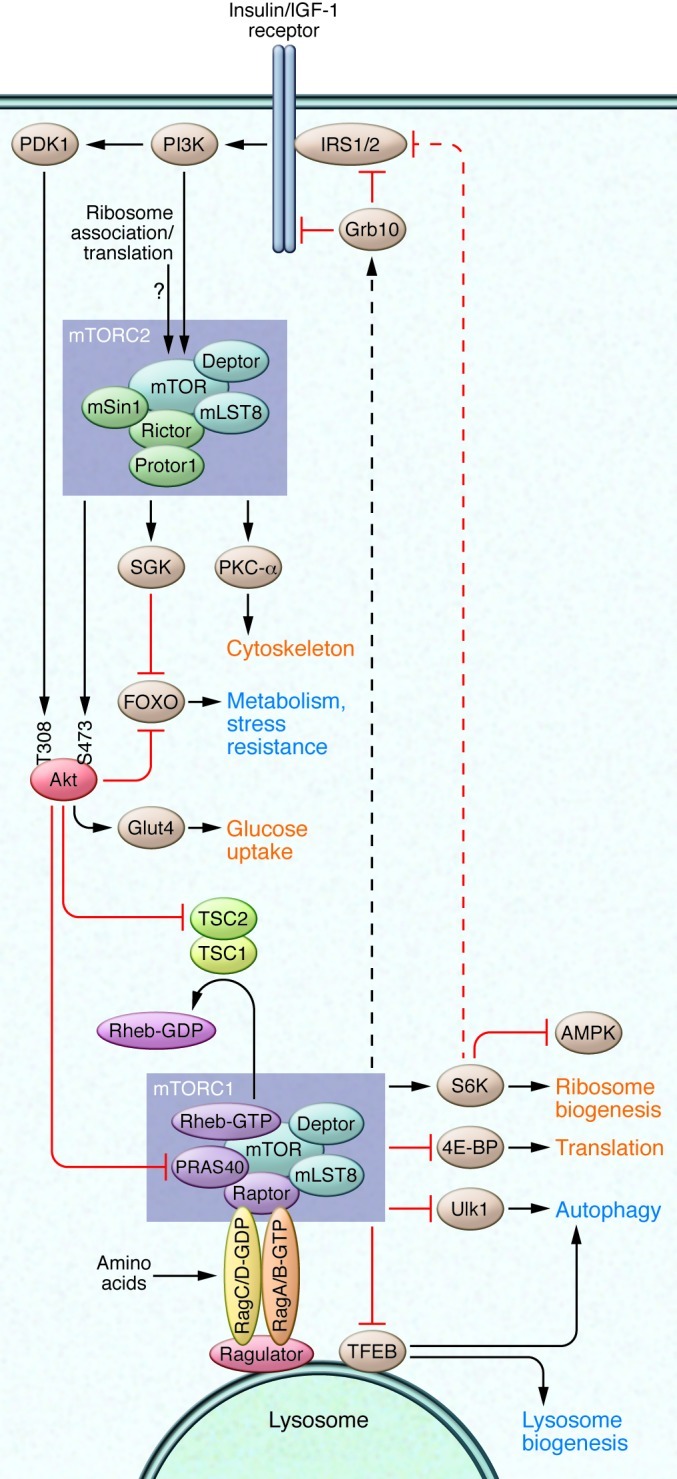
mTOR is found in two complexes, mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTORC1 is regulated in part via the TSC complex, which normally act as a GTPase-activating protein for Rheb to suppress mTORC1 signaling. mTORC1 is also regulated by amino acids via the Ras-related GTP binding (Rag) family of small GTPases. The Rag proteins activate mTORC1 by localizing mTORC1 to the lysosome via interaction with the ragulator complex (110). mTORC1 promotes growth by enhancing ribosomal biogenesis, translation, and other anabolic processes, while inhibiting autophagy. mTORC1 suppresses insulin/IGF-1 signaling via direct regulation of Grb10 and S6K, which subsequently reduces signaling to mTORC2. AKT, an inhibitor of TSC1/2, is one of several direct substrates of mTORC2. Processes that are upregulated by mTOR signaling are shown in red; those that are downregulated by mTOR signaling are shown in blue.
