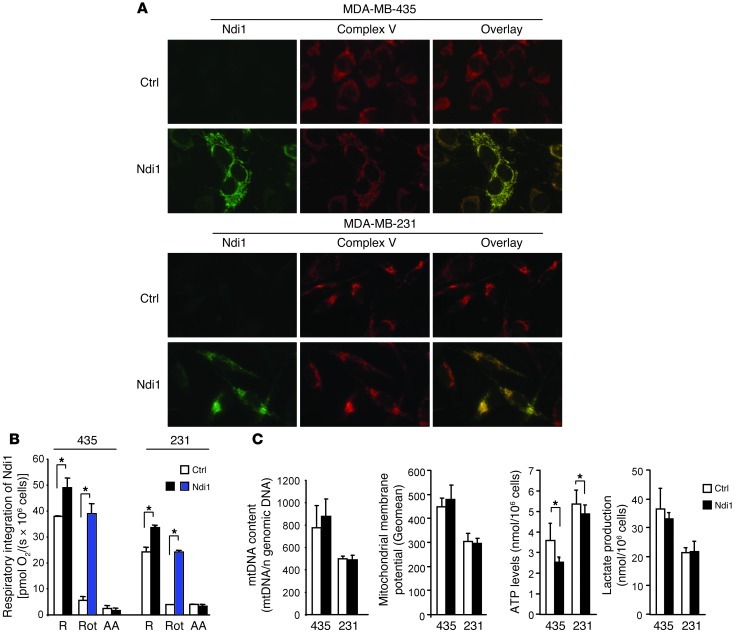
Figure 1. Enhancement of mitochondrial complex I activity by integration of Ndi1: metabolic characterization.
(A) Ndi1 expressed in MDA-MB-435 and MDA-MB-231 human cancer cells upon lentiviral transduction localized to mitochondria, as shown by dual label immunocytochemistry. Control cells (Ctrl) were transduced with empty vector. Shown are Ndi1 (green), mitochondrial complex V (red), and merged (yellow) staining patterns of the same representative fields. Original magnification, ×20. (B) Ndi1 was integrated into the mitochondrial respiratory chain and enhanced tumor cell respiration. Respiration of MDA-MB-435 and MDA-MB-231 (denoted “435” and “231,” respectively) control and Ndi1-expressing cells, measured by oxygen consumption. R, routine respiration; Rot, rotenone (mammalian complex I inhibitor); AA, antimycin A (complex III inhibitor). All parameters were measured by high-resolution respirometry in intact cells. (C) Effects of Ndi1 expression on cellular metabolism in MDA-MB-435 and MDA-MB-231 cells. mtDNA content was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR and referenced to nuclear genomic DNA. Mitochondrial membrane potential was analyzed by flow cytometry and expressed as geometric mean of the signal. ATP levels were measured by ATP-dependent luciferase activity. Lactate production was measured by fluorometry. Data are mean ± SEM (n = 3). *P < 0.05, unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test.