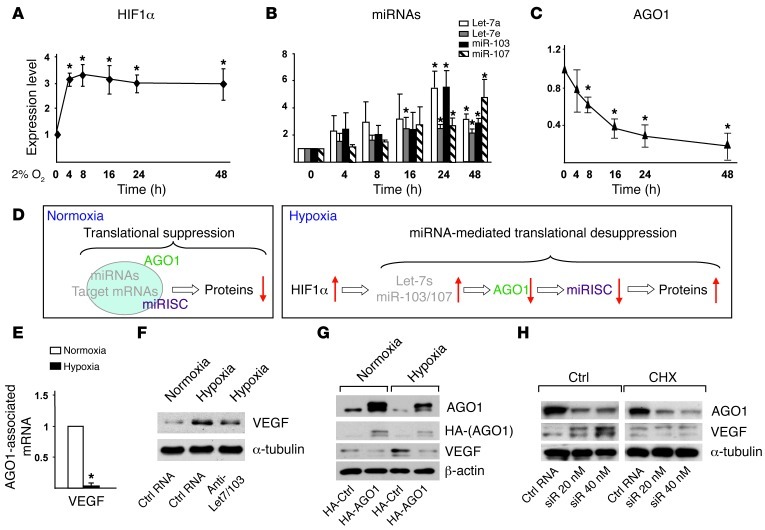
Figure 4. Translational desuppression of VEGF caused by AGO1 targeting.
(A–C) HUVECs were subjected to normoxia or hypoxia for the indicated times. Western blot analysis of protein levels of HIF1α (A) and AGO1 (C) and TaqMan qPCR analysis of miRNAs (B). (D) Model of translational suppression under normoxia and desuppression under hypoxia. Red arrows indicate up- or downregulation of various molecules. (E) AGO1-associated mRNAs were enriched by IP. Level of VEGF was detected by qPCR. (F) HUVECs were transfected with a mixture of anti–Let-7a/e/miR-103 (10 nM each) or control RNA (30 nM). (G) HUVECs were transfected with a control vector expressing HA or HA-AGO1-ORF plasmid containing AGO1 ORF without 3′ UTR. (H) HUVECs were transfected with AGO1 siRNA or control RNA for 48 hours, then treated with vehicle control or cycloheximide (CHX) (5 μg/ml) for 4 hours. Cells in F–H were then subjected to hypoxia or kept as normoxia controls, and various proteins were detected by Western blot analysis. *P < 0.05 compared with normoxia group.