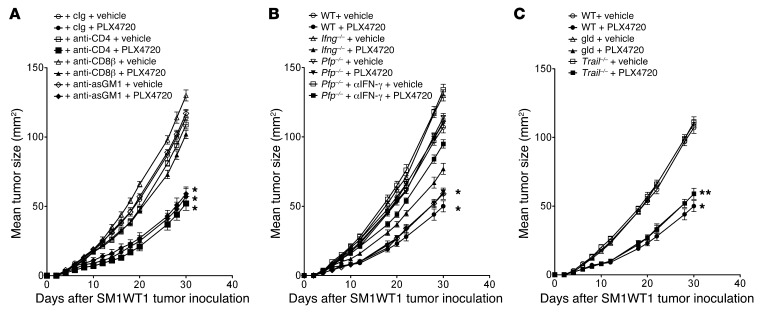
Figure 6. PLX4720 antitumor activity is CD8+ T cell dependent.
(A) Groups of 5 WT mice were inoculated with 5 × 105 SM1WT1 cells. Mice received vehicle or PLX4720 (20 mg/kg i.p.) daily from day 3 to 10 after tumor inoculation. Some groups of mice were additionally treated with cIg, anti-CD4, anti-CD8β, or anti-asialoGM1 (100 μg i.p. each) on days 2, 3, 10, 17, and 24 after tumor inoculation to deplete T cell subsets or NK cells. (B) Groups of 5 WT, Ifng–/–, or Pfp–/– mice were inoculated with 5 × 105 SM1WT1 cells. Mice received vehicle or PLX4720 (20 mg/kg i.p.) daily from day 3 to 10 after tumor inoculation. Some groups of Pfp–/– mice were additionally treated with anti–IFN-γ (250 μg i.p.) on days 2, 3, 10, 17, and 24 after tumor inoculation to neutralize IFN-γ. (C) Groups of 5 WT, gld, or Trail–/– mice were inoculated with 5 × 105 SM1WT1 cells. Mice received vehicle or PLX4720 (20 mg/kg i.p.) daily from day 3 to 10 after tumor inoculation. Tumor sizes are represented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical differences in tumor sizes between mice treated with vehicle and those treated with PLX4720 therapy for each group were determined by a Mann-Whitney test (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01). Data are representative of 2 independent experiments.