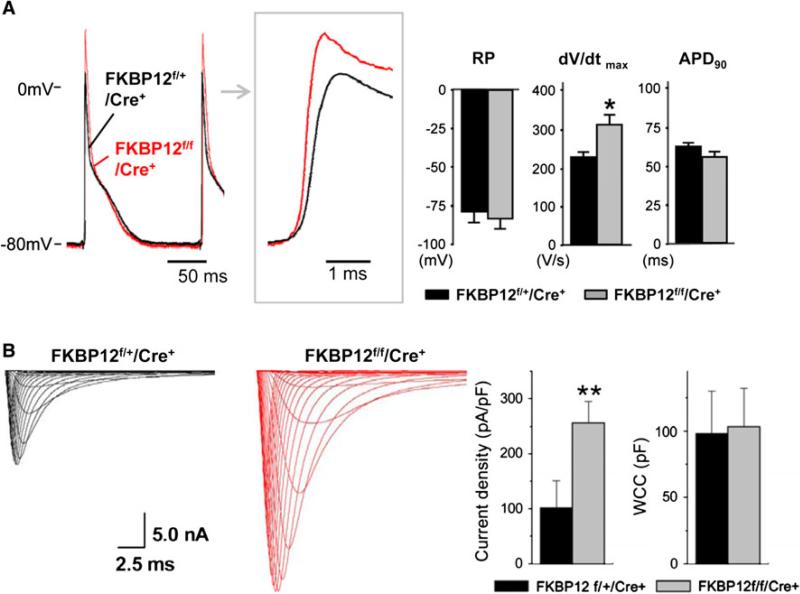
Fig. 2.
Cellular electrophysiologic analyses of FKPB12f/f/MHC-Cre+ and FKBP12f/+/MHC-Cre+ hearts. a Representative ventricular transmembrane APs recorded from an FKBP12f/f/MHC-Cre+ and an FKBP12f/+/MHC-Cre+ heart. The maximum upstroke velocity of phase 0 of the AP (dV/dt)max and the peak action potential amplitude were increased in FKBP12f/f/MHC-Cre+ hearts compared with control hearts. The means of RP and APD90 were similar between FKBP12f/f/Cre+ and FKBP12f/+/Cre+ hearts, *p < 0.05. b INa traces recorded from isolated FKBP12f/f/MHC-Cre+ and control FKBP12f/+/MHC-Cre+ ventricular cardiomyocytes. The maximal peak INa in FKBP12f/f/MHC-Cre+ myocytes was increased more than 2.5-fold compared with FKBP12f/+/MHC-Cre+ cells (15 cells/6 hearts), **p < 0.01