Figure 1.
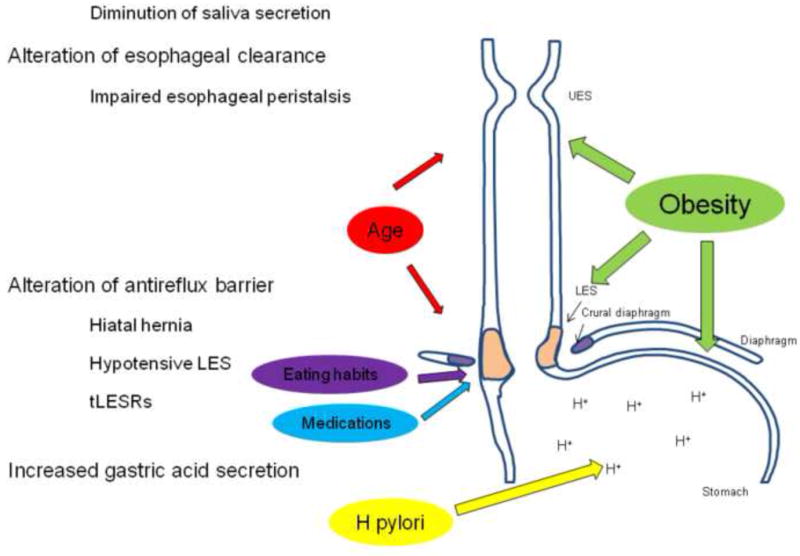
The environmental factors interact with the different mechanisms involved in GERD pathogenesis. Obesity alters esophago-gastric junction (EGJ) integrity, esophageal peristalsis and increases intra-gastric pressure. Age modifies EGJ integrity and impairs esophageal clearance by altering esophageal peristalsis and decreasing saliva secretion. Eating habits and medications decrease lower esophageal sphincter pressure (LES), increase the number of transient LES relaxations and delay gastric emptying. Helicobacter pylori modifies acid gastric secretion.
