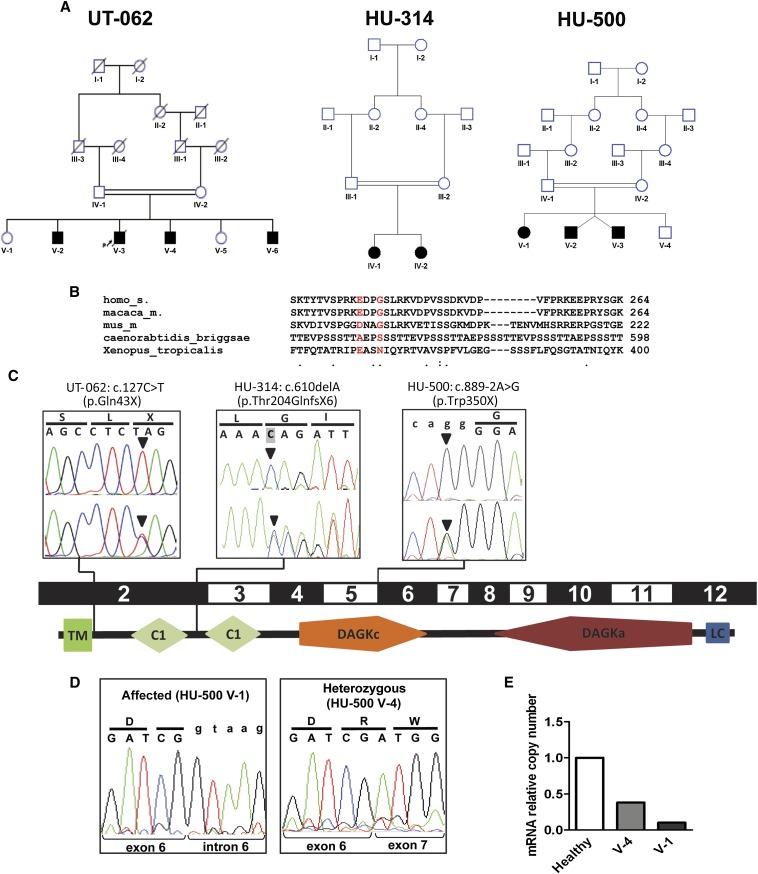
Figure 1.
Representation of the pedigrees described in this study and of the DGKE mutations in relation to the gene exon structure and protein domains. (A) Pedigrees of families UT-062, HU-314, and HU-500. Squares represent males, circles represent females. Black filled symbols indicate the affected status. Double-horizontal bars indicate consanguinity. (B) Sequence alignment across different species of the GPRIN1 gene in correspondence of the two sequence variants detected by exome sequencing in the affected individuals of family UT-062. The reference amino acids are represented in red. Dots on the bottom line represent medium (:) and low (.) evolutionary conservation. The absence of a dot indicates absence of evolutionary conservation. Numbers indicate the position of the last represented amino acid in the corresponding protein. (C) Chromatograms of the three different mutations in the gene DGKE (arrowheads) in the representative affected individuals from the consanguineous pedigrees UT-062, HU-314, and HU-500, in relation to the corresponding coding exons and schematic representation of human DGKε protein structure (according to SMART, http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de). Pedigree identifiers and mutations are reported above the boxes. Upper chromatograms report the homozygous mutations in one affected sibling per each pedigree. Lower chromatograms show the heterozygous mutations in one of the parents from each family. Codons and the corresponding translated amino acids are displayed above the chromatograms. Lowercase letters indicate the intronic sequence. Shading of the first base of the second codon in HU-314 chromatogram indicates the deleted base. (D) Chromatograms of the RT-PCR on mRNA obtained from peripheral leukocytes of one affected individual (V-1) and a heterozygous sibling (V-4) of family HU-500. Intron 6 is retained in the presence of homozygous mutation (left panel), resulting in the transcription of the intron (lowercase letters). Note that in the heterozygous sibling (right panel), only the wild-type allele is detectable, indicating that the amount of mutated mRNA is very low compared with the wild type. Codons and the corresponding translated amino acids are displayed above the chromatograms. Lowercase letters indicate the intronic sequence. (E) Relative quantitation by real-time PCR of the number of DGKE transcripts in leukocytes from an healthy individual, an heterozygous carrier, and the homozygous affected individual HU-500 V-1 showing that the mutated transcript undergoes non-sense–mediated decay. TM, transmembrane domain; C1, protein kinase C conserved region (C1 domain); DAGKc, diacylglycerol kinase catalytic domain; DAGKa, diacylglycerol kinase accessory domain; LC, low complexity region.