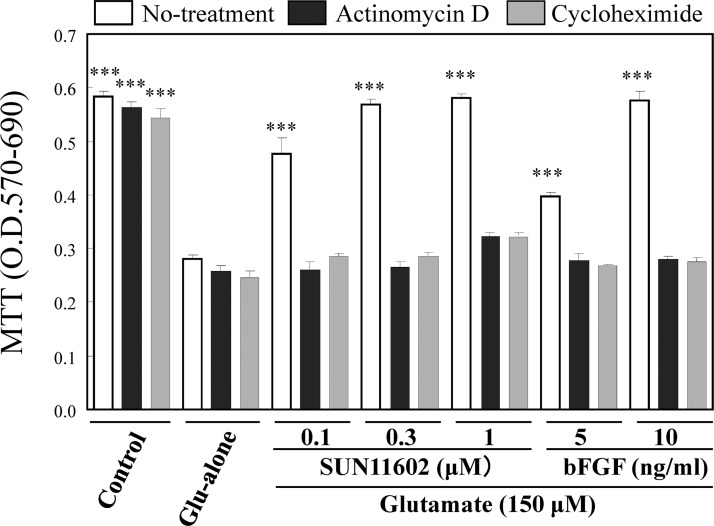
Figure 2.
Neuroprotective effects of SUN11602 and basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) against glutamate-induced toxicity (150 μM) in primary cultures of rat cerebrocortical neurons. The open bars reveal that the effectiveness of SUN11602 and bFGF is ascribed to unimpaired protein synthesis, by which they can activate their neuroprotective mechanisms. Their neuroprotective effects were abolished by treatment with either actinomycin D (1 μg/mL, black bar) or cycloheximide (1 μg/mL, gray bar), which can interfere with transcription or translation, respectively. Actinomycin D or cycloheximide was first added to the cultures, and, 2 h later, SUN11602 or bFGF was added. After a 24 h incubation, neurons in the cultures were exposed to 150 μM glutamate for another 24 h, and cell viability was determined by a (3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. ***p < 0.001 compared to glutamate alone (means ± SEM, n = 6, Dunnett’s multiple comparison test).