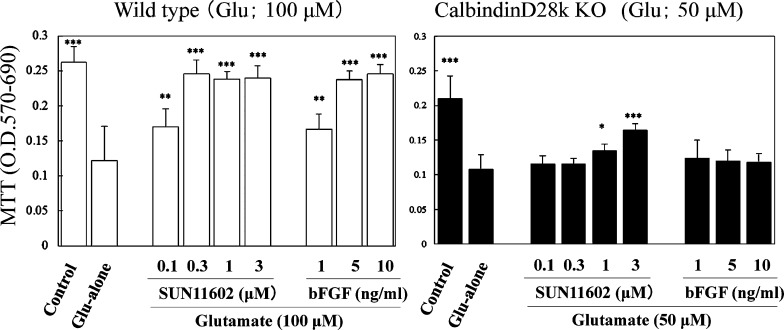
Figure 6.
Neuroprotective effects of SUN11602 and bFGF against glutamate-induced toxicity in primary cultures of cerebrocortical neurons from WT and Calb–/– mice. These data indicate that calbindin-D28k in WT mice may play important roles in the neuroprotective mechanisms by SUN11602 and bFGF. In Calb–/– mice, the molecular function of calbindin-D28k was mostly diminished, although there was a slight improvement in neuroprotection with higher concentrations of SUN11602. Following the 24 h incubation with SUN11602 and bFGF, the cultures were exposed to either 100 or 50 μM glutamate for another 24 h, and cell viability was then determined by MTT assay. The toxic concentrations of glutamate (100 or 50 μM) were employed for which those concentrations were suitable for the cultures in order to react sensitively and appropriately. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 compared to the glutamate group (means ± SEM, n = 6, Dunnett’s multiple comparison test).