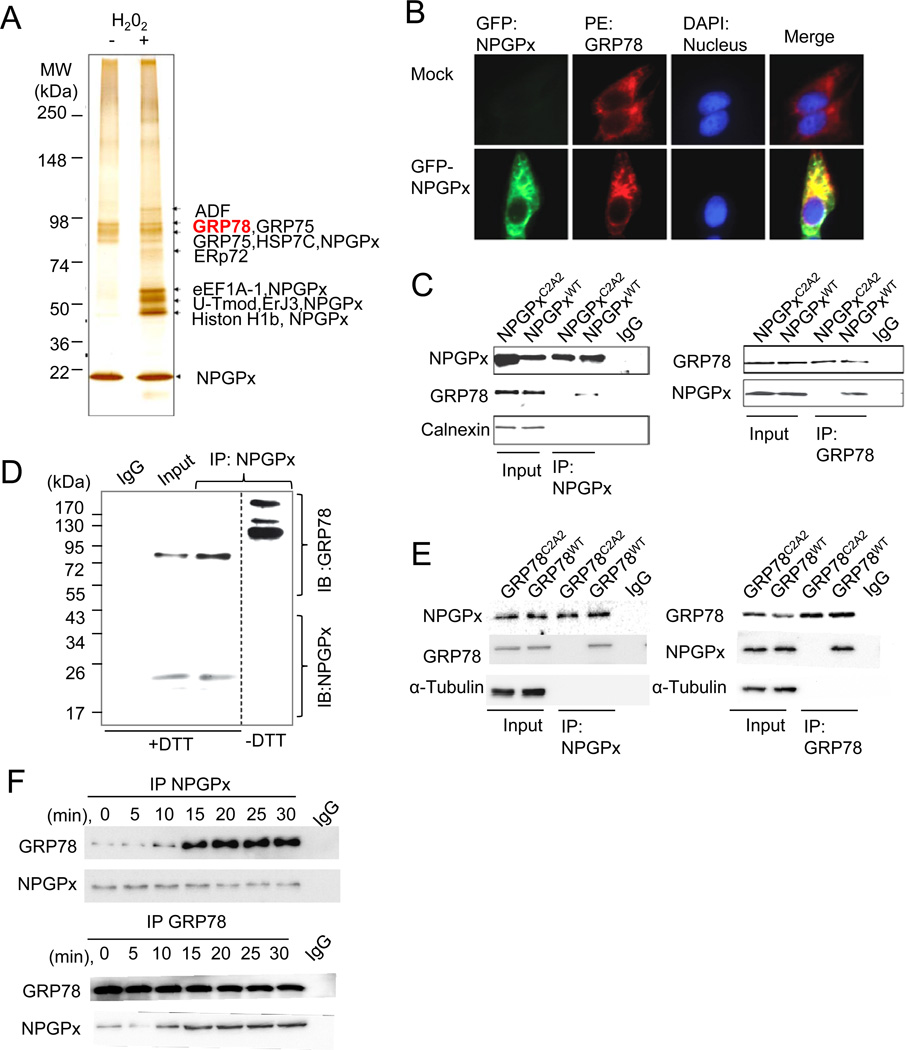
Figure 4. NPGPx covalently interacts with GRP78 in cells under oxidative stress.
(A) Identification of NPGPx-interacting proteins pulled down from the NPGPx affinity column. (B) Immunofluorescent staining of MEFs transduced with or without (mock) GFP-NPGPx: MEFs were stained with GRP78 antibody (red) and DAPI (blue) (C) Reciprocal IP of NPGPx and GRP78 using NPGPx−/− MEFs ectopically expressing WT or C2A2 NPGPx. NPGPx, GRP78, and calnexin were probed. (D) IP proteins of NPGPx and GRP78 were subsequently analyzed by Western blot in reducing (+DTT) or non-reducing (−DTT) conditions. NPGPx and GRP78 were probed as indicated. Under non-reducing conditions, NPGPx covalently interacts with GRP78, resulting in high molecular weight bands containing NPGPx. (E). Reciprocal IP of NPGPx and GRP78 in MEFs reconstituted with hGRP78WT or hGRP78C2A2. Precipitated proteins were subsequently analyzed by Western blot analysis. (F) Reciprocal IP of NPGPx and GRP78 in lysates prepared using WT MEFs treated with H2O2 for the indicated duration. Immunoprecipitated proteins were subjected to Western blot analysis.