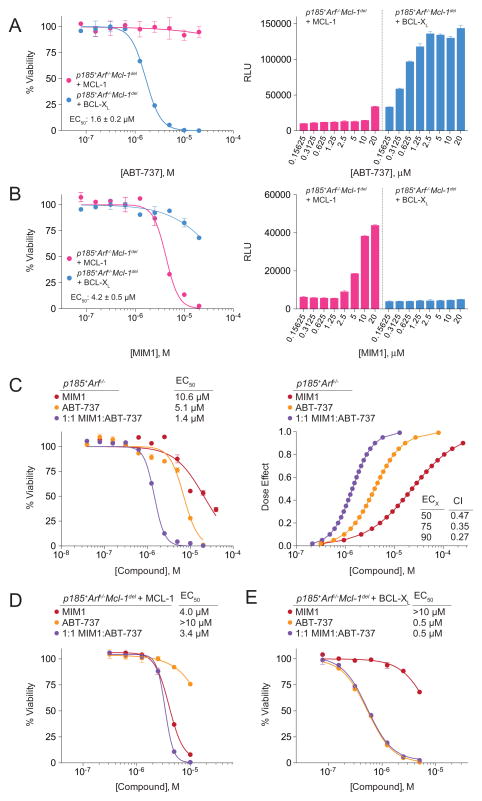
Figure 6. MCL-1-dependent Anti-leukemia Activity of MIM1 and Synergy with ABT-737.
(A) ABT-737 selectively impaired the viability of p185+Arf−/−Mcl-1-deleted B-ALL cells rescued by BCL-XL, but not MCL-1, as measured by CellTiter-Glo assay at 24 h. The selective cytotoxic effect of ABT-737 was accompanied by dose-responsive caspase 3/7 activation in the BCL-XL-rescued leukemia cell line, as measured at 8 h post-treatment.
(B) MIM1 exhibited the opposite cellular activity profile of ABT-737, selectively impairing the viability of p185+Arf−/−Mcl-1-deleted B-ALL cells rescued by MCL-1, but not BCL-XL. Correspondingly, the selective cytotoxic effect of MIM1 was accompanied by dose-responsive caspase 3/7 activation only in the MCL-1-rescued leukemia cell line.
(C) Combination treatment with MIM1 and ABT-737 induced synergistic killing of parental p185+Arf−/− B-ALL cells that express endogenous MCL-1 and BCL-XL, as reflected by a leftward shift of the viability isotherm (left) and the CalcuSyn dose effect curve (right), with calculated CI values of <1 at ED50, ED75, and ED90. CI, combination index; ED, effective dose.
(D) The addition of ABT-737 to MIM1 treatment of MCL-1-rescued p185+Arf−/−Mcl-1-deleted B-ALL cells had little to no additional cytotoxic effect, consistent with the relative inactivity of ABT-737 in the context of MCL-1-dependence.
(E) Correspondingly, the addition of MIM1 to ABT-737 treatment of BCL-XL-rescued p185+Arf−/−Mcl-1-deleted B-ALL cells provided no additional cytotoxic effect, consistent with the relative inactivity of MIM1 in the context of BCL-XL-dependence.
Data are mean ± SEM for experiments performed in at least duplicate, normalized to vehicle control, and repeated twice with independent cell cultures with similar results. See also Figure S3.