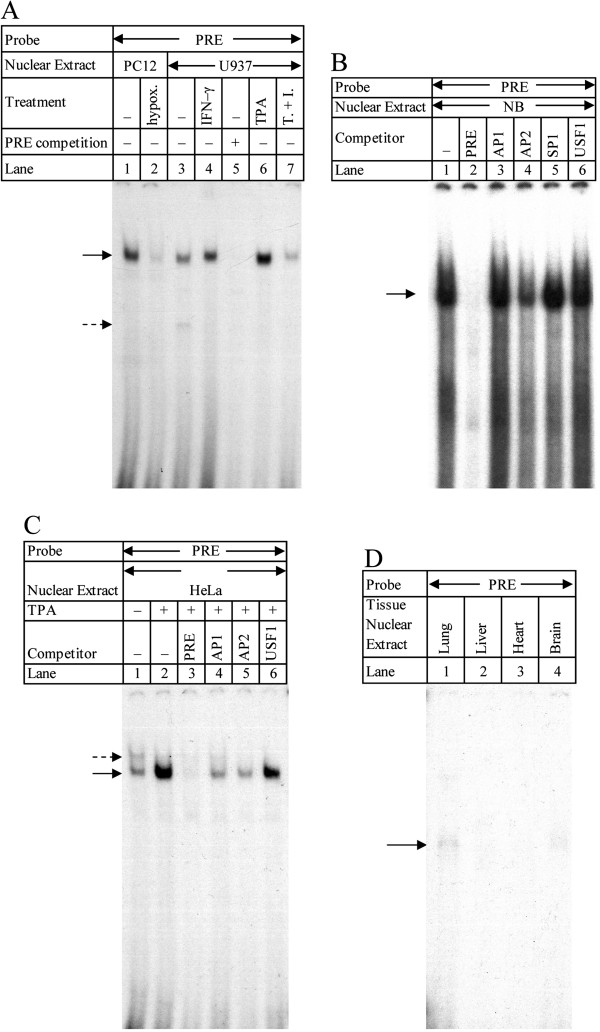
Figure 1.
EMSA in stimulated and unstimulated cell culture nuclear extracts and vs. various transcription factor binding oligomers. A. Radiolabeled PRE was incubated with PC12 or U937 nuclear extracts. PC12 extracts were either normal (lane 1) or from cells subject to hypoxia (lane 2). U937 extracts were either normal (lanes 3, 6) or from INF-γ induced (lane 4), TPA-induced (lane 6), or TPA + INF-γ induced cells (lane 7). In addition, one sample of normal U937 extract was incubated both with labeled and 200x molar excess of unlabeled PRE (lane 5). Arrows indicate major DNA-protein interactions. B, C. The PRE fragment from plasmid pβXbB was radiolabeled and incubated in NB or HeLa cell nuclear extracts with or without 200x molar excess competition against oligomers known to bind specific transcription factors. DNA-protein interactions are indicated with arrows. B. NB cell nuclear extracts. No competition (lane 1), competition vs. unlabeled PRE (lane 2), competition vs. unlabeled oligomers that bind AP1 (lane 3), AP2 (lane 4), SP1 (lane 5), or USF1 (lane 6). C. HeLa (lane 1) or TPA-stimulated HeLa (lanes 2–6) nuclear extracts. Reactions were subjected to no competition (lanes 1–2) competition vs. 200x molar excess of unlabeled PRE fragment (lane 3), AP1-binding oligomer (lane 4), AP2-binding oligomer, or USF-binding oligomer (lane 5). D. EMSA of the PRE in four human tissue nuclear extracts. The DNA fragment corresponding to the PRE (−76/-47) was purified from plasmid pβXbB, radiolabeled, and incubated in nuclear extracts from human lung (lane 1), liver (lane 2), heart (lane 3), or brain (lane 4). DNA-protein interaction band is indicated by arrow. Unbound probe ran at the bottom of the gel (not shown).