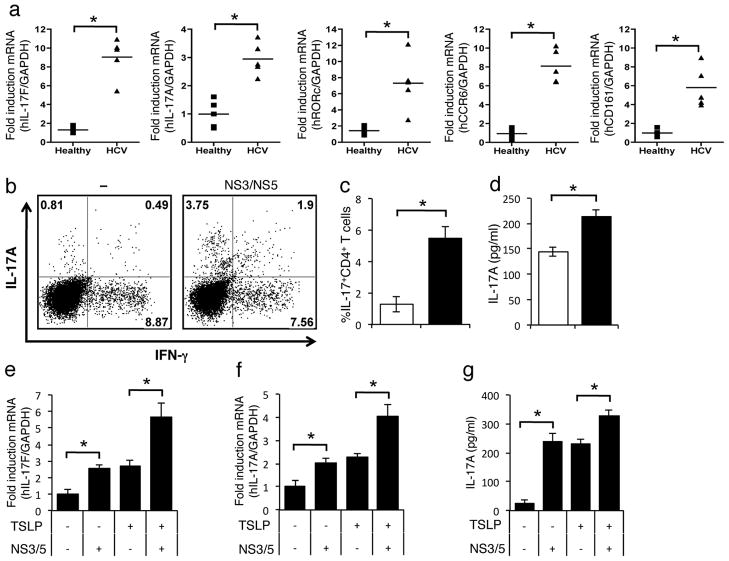
Figure 6. Direct action of TSLP enhance IL-17 production by PBMC from HCV-infected patients.
(a) CD4+ T cells were isolated from PBMC of healthy and chronic HCV patients. Expression levels of mRNA encoding IL-17A, IL-17F, RORc, and CCR6 were quantified using real-time PCR. (b, c, d) CD4+ T cells were cocultured for 7 days by DCs activated with 5 μg/ml mixed-NS3/NS5 or medium alone. T cells were restimulated with PMA plus ionomycin after 7 days of coculture. Production of IL-17, and IFNγ was determined by intracellular cytokine staining (b). c) Bar graph show the percentage of IL-17-producing cells in total CD4+ cells. d) Cytokine production was measured in the culture supernatant by ELISA. Data shown are the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (c, d) or one experiment representative of three independent experiments with similar results (b). Purified CD4+ T cells from PBMC of HCV-infected patients were stimulated with 5 μg/ml mixed-NS3/NS5 or medium alone, either presense or absense of recombinant TSLP antibody (5 ng/ml). Cells were harvested after 72 hours culture. Expression levels of mRNA encoding IL-17A, IL-17F were quantified using real-time PCR (e, f). Production of IL-17 was measured in the culture supernatant using ELISA (g). Data represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments.