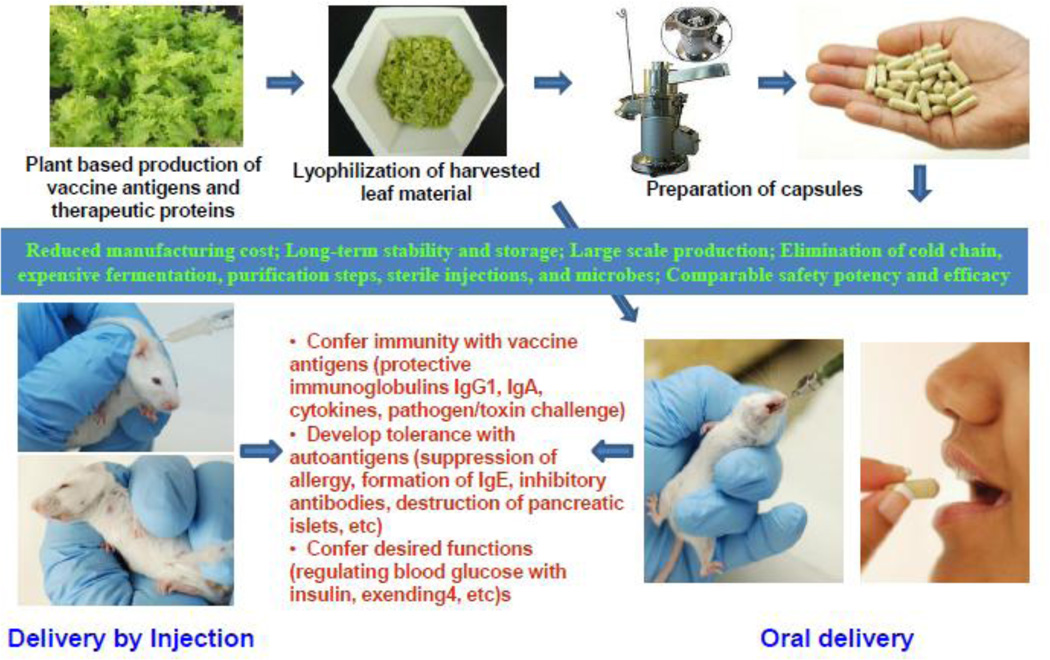
Fig. 1.
An outline of the process of oral delivery of plant-derived vaccine antigens and biopharmaceuticals. Foreign genes are first expressed in lettuce chloroplasts by bombardment of leaves with chloroplast vectors using the gene gun. After confirmation of stable integration of foreign genes into all of the chloroplast genomes in each plant cell and expression of the correct size protein and functionality, genetically modified lines are transferred to the greenhouse for increasing biomass. Harvested leaves are lyophilized, powdered and stored in moisture free environment. Machines are commercially available for processing lyophilized leaf materials into desired particle size and packaging into capsules. Evaluation process includes microbial count in lyophilized materials, integrity of therapeutic proteins after prolonged storage (folding with disulfide bonds, pentameric or multimeric structures) and functionality by conferring immunity with vaccine antigens (protective immunoglobulins IgG1, IgA, cytokines, pathogen/toxin challenge) or developing tolerance with autoantigens (suppression of allergy, formation of IgE, inhibitory antibodies, destruction of pancreatic islets, etc) or conferring desired functions (regulating blood glucose with insulin, exendin-4, etc).