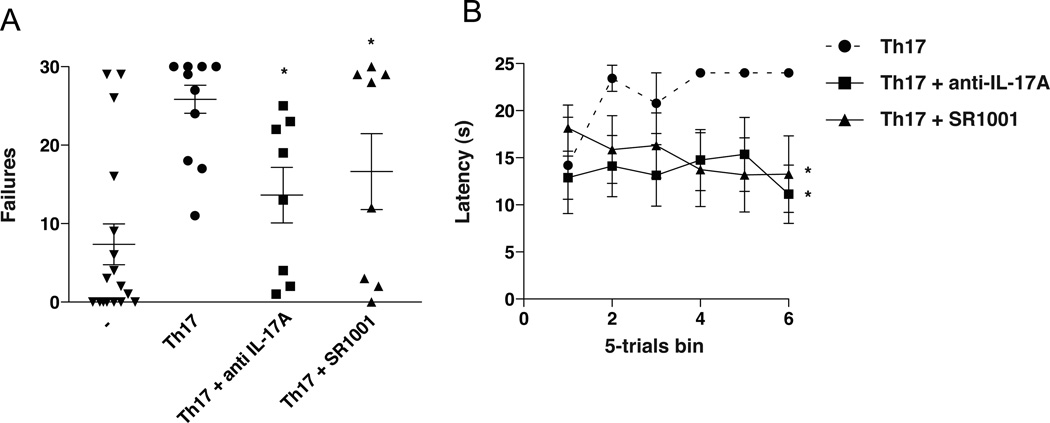
Figure 4.
Inhibiting RORγT or IL-17A has antidepressant effects in Th17-dependent learned helplessness. Wild-type mice pretreated where indicated with anti-IL-17A antibodies or SR1001, a RORγT inhibitor, received Th17 cells. (A–B) Mice were subjected to reduced intensity IES, and 24 h later tested with escapable foot shocks. (A) Escape failures after reduced IES. Each symbol represents total escape failures in 30 trials for an individual mouse, bars represent group means (n=8–10 mice/group, ANOVA *p<0.05 compared with untreated Th17 recipient mice, df=45, F=8.220). (B) Average escape latency during 5-trial blocks after reduced intensity IES. Mice receiving Th17, Th17+ anti-IL17A, and Th17 + SR1001 mice had an average of 21.8±1.6, 13.6±0.6 and 15.1±0.8 sec escape latency, respectively. (n=8–10 mice/group, ANOVA *p<0.05 compared with untreated Th17 recipient mice, df=17, F=15.77).