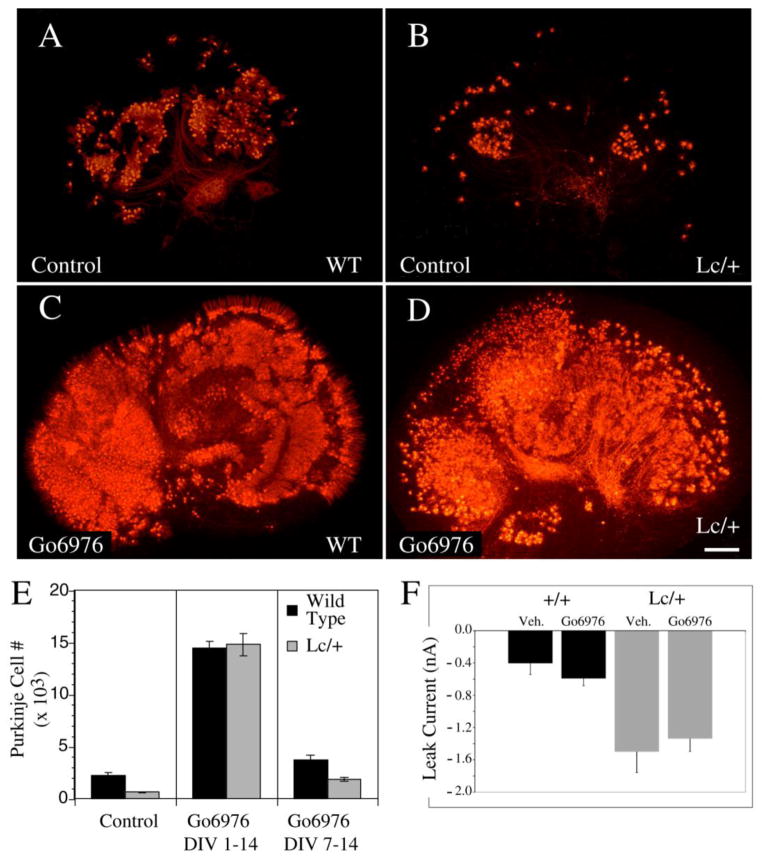
Figure 4.
Treatment of both WT and Lc/+ cerebellar slice cultures with the conventional PKC inhibitor Gö6976 (1μM) from 0 to 14 DIV dramatically increases PC survival. A–D) The images of calbindin labeled control (A and B) and Gö6976-treated (C and D) WT (A, C) and Lc/+ (B, D) cerebellar slices demonstrates the dramatic increase in the number of surviving PCs after 14 DIV due to ongoing treatment with Gö6976 (Scale bar 200μm). E) Treatment with Gö6976 dramatically increases both WT and Lc/+ PC survival when cultures are treated from the first day in vitro. However, delaying Gö6976 treatment until 7 DIV to 14 DIV still significantly increases WT and Lc/+ PC survival, although the effects are not as dramatic. F) Measurement of the leak current in WT and Lc/+ PCs did not show any evidence that treatment with Gö6976 has long term effects on the leak current induced by the mutant GluRδ2Lc channel. Lc/+ PCs had larger leak currents whether or not they had been treated with Gö6976.