Fig. 1.
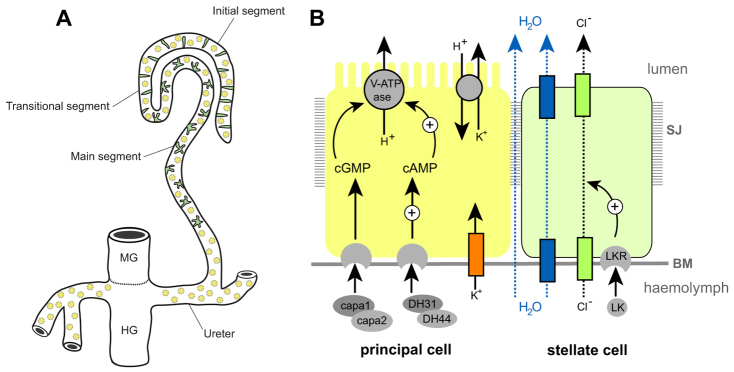
Drosophila Malpighian tubules. (A) The four MpTs consist of initial, transitional and main segments, and a ureter. Stellate cells (SCs, green) are interspersed with principal cells (PCs, yellow) in the initial and transitional segments (where they are bar shaped), and throughout the secretory region of the main segment (where they are stellate). (B) The major physiological activities carried out by PCs (yellow) and SCs (green). Ion transport is driven by a H+-transporting vacuolar-ATPase (V-ATPase) on the luminal membrane of PCs, which, coupled with a cation/H+ antiporter, transports potassium ions into the lumen. Chloride ions move down an electrochemical gradient through chloride channels in SCs. Water (blue arrows) follows by osmosis through water channels in SCs and paracellular routes. Capability peptides 1/2 (Capa) and diuretic hormone 31/44 (DH) stimulate urine production through cGMP and cAMP pathways in PCs (Cabrero et al., 2002; Coast et al., 2001; Johnson et al., 2005; Kean et al., 2002). BM, basement membrane; LK, leucokinin; LKR, leucokinin receptor; SJ, septate junction.
