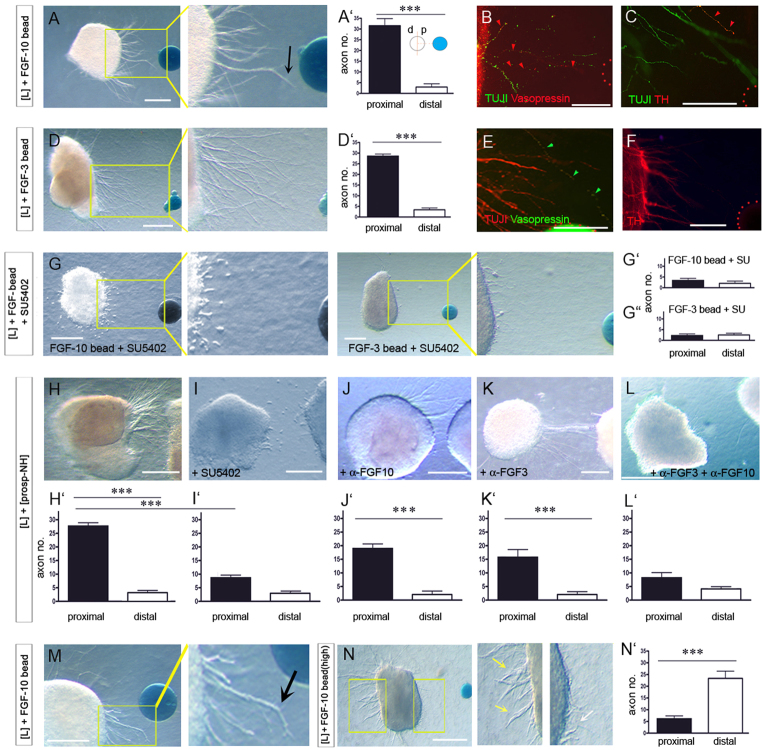
Fig. 3.
FGFs orient H-NH axons. (A,A′,D,D′) Chick [L] explants cultured with protein-soaked beads shown in whole-mount view (A,D). Significantly more (***P<0.0001) axons extend from the proximal (p) versus distal (d) face of [L] explants (A′,D′). (B,C,E,F) High-powered views of boxed regions in A,D, after immunolabelling. Axons, including those expressing Vasopressin and TH (arrowheads) project from [L] explants towards Fgf10- (B,C) or Fgf3- (E,F) soaked beads. (Beads outlined by red dots.) (G-G″) Treatment with SU5402 abolishes FGF-stimulated outgrowth. (H-L′) [L] explants cultured with prosp-NH explants alone (H,H′) or with inhibitors (I-L′). (M) Local chemorepulsion (arrow) in proximity to an Fgf10-soaked bead. (N,N′) [L] explants cultured with high concentrations of FGF. In high powered views (N) white arrow points to short axons that emerge from proximal face, yellow arrows point to axons emerging from distal face. Error bars represent s.e.m. ***P<0.005. d, distal; p, proximal. Scale bars: 100 μm in A,D,G,H-L,M,N; 50 μm in B,C,E,F.