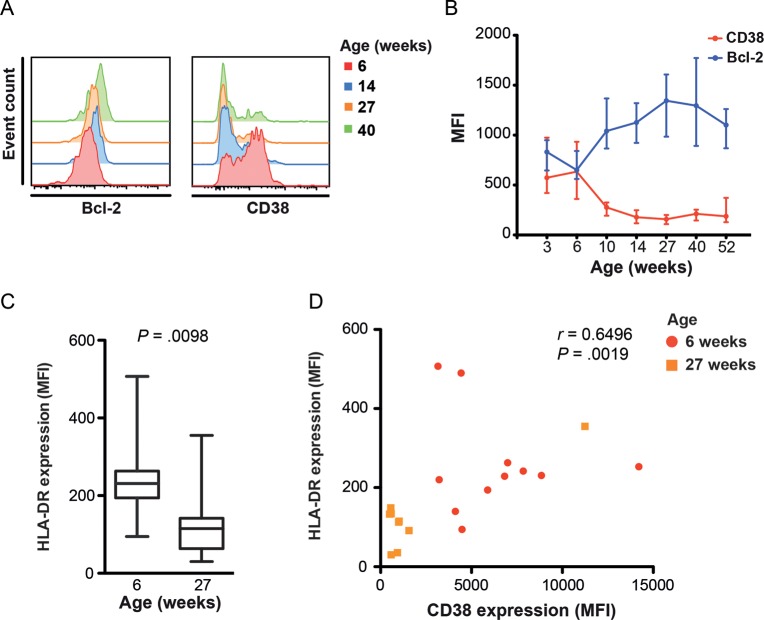
Figure 2.
Longitudinal changes in BCG-specific T-cell expression of antiapoptotic and activation markers during the first year of life. Expression of Bcl-2, CD38, and HLA-DR by cytokine-expressing BCG-specific CD4+ T cells was measured by whole-blood intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry. A, Histograms from a representative individual infant showing changes in Bcl-2 and CD38 expression levels in total cytokine-expressing BCG-specific CD4+ T cells (combined interferon γ [IFN-γ], interleukin 2 [IL-2], tumor necrosis factor α [TNF-α], and/or interleukin 17 [IL-17] expression). B, Changes in Bcl-2 and CD38 expression levels, represented as median fluorescence intensity (MFI), by BCG-specific CD4+ T cells. The line represents the median, and error bars represent the interquartile range. C, HLA-DR expression levels, represented as MFI, by BCG-specific CD4+ T cells at 6 and 27 weeks after vaccination. The horizontal line represents the median, the box represents the interquartile range, and the whiskers represent the range. Because HLA-DR expression was only measured at 6 and 27 weeks of age, no Bonferroni adjustment was applied to this comparison. D, Association between HLA-DR and CD38 expression levels by cytokine-expressing CD4+ T cells 6 and 27 weeks after vaccination. The strength of the correlation was calculated using the Spearman rank correlation test.