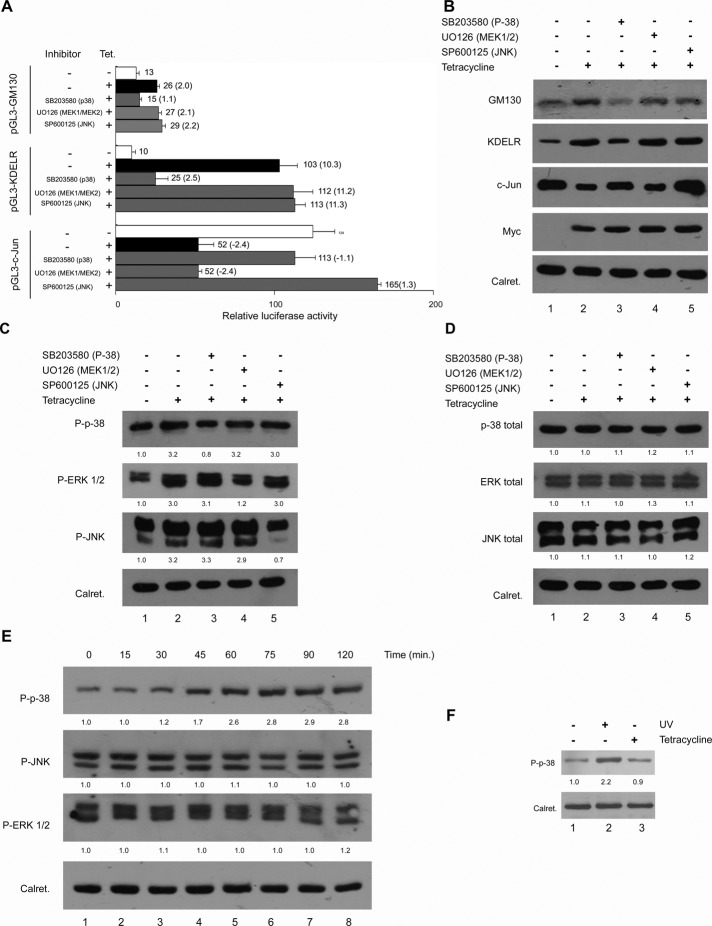
FIGURE 5:
Analysis of the MAPK pathways and the effect of their inhibitors on the T-Rex Rab1b cells. Inhibitors used were SB203580 (p-38), UO126 (MEK1/2), and SP600125 (JNK). (A) Effect of specific MAPK inhibitors on the relative luciferase activities of the pGL3-GM130, pGL3-KDELR, and pGL3-c-JUN constructs depicted in Figure 4A. Numbers on the right of each bar indicate the average value of relative luciferase activity from at least three experiments, and the ratio between samples for the indicated condition is shown in parentheses. Error bars represent SD. (B) Effect of specific MAPK inhibitors on the GM130, KDELR, and c-JUN changes induced by the increase in Rab1b. (C and D) Effect of Rab1b induction and MAPK inhibitors on the phosphorylation and total levels of p38, JNK, and ERK. The intensity of each band relative to calreticulin (loading control) was measured, and the fold change was calculated as the ratio of the tetracycline induced to the uninduced one. Numbers under each MAPK Western blot represent the average fold change of two independent experiments. Inhibitors of p38 and MEK1-2: 25 μM; JNK inhibitor: 50 μM. (E) Time course of the activation of the indicated phospho-MAPK in T-Rex Rab1b cells after different times of tetracycline addition. Numbers under each MAPK Western blot represent the average fold change of two independent experiments. Fold change was calculated as indicated in (C) and (D). (F) p38 phosphorylation analysis in response to tetracycline addition. P-p38 was analyzed in untransfected HeLa cells incubated in regular medium (lane 1), in cells irradiated with UV (to stimulate P-p38 induction, lane 2) and in the presence of tetracycline (lane 3).