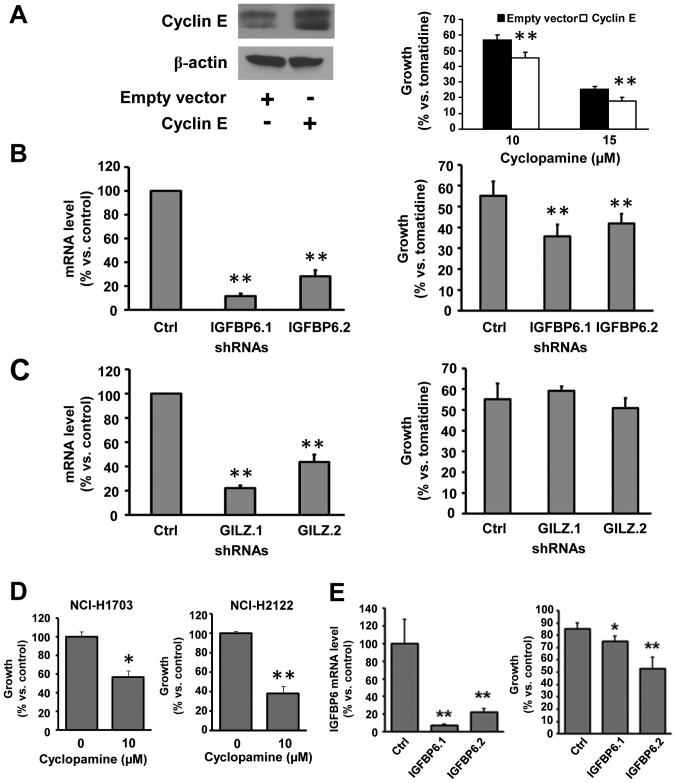
Figure 2.
Functional validation of species associated with Smo-mediated growth inhibition. (A) Cyclin E was overexpressed in C-10 murine immortalized lung epithelial cells (left panel). Cyclin E overexpression enhanced response to cyclopamine treatment versus tomatidine controls (right panel). (B) IGFBP6 knock-down in ED-1 lung cancer cells (left panel) increased response to cyclopamine treatment versus controls (ctrl) (right panel). (C) GILZ knock-down in ED-1 cancer cells (left panel) did not significantly affect cyclopamine response (right panel). (D) Independent treatments of the human lung cancer cell lines NCI-H1703 (left panel) and NCI-H2122 (right panel) with cyclopamine (10 μM) for three days reduced cell growth versus vehicle control. Basal IGFBP6 levels were at the lowest limit of detection by real-time PCR assays in NCI-H1703 cells (data not shown), consistent with the enhanced sensitivity of these cells to cyclopamine. (E) Higher IGFBP6 levels were detected in NCI-H2122 relative to NCI-H1703 cells. When IGFBP6 expression was knocked-down by transfection of two independent siRNAs (left panel), the sensitivity of NCI-H2122 to cyclopamine (10 μM) was enhanced (right panel). Standard deviation bars are shown. *P<0.05; **P<0.01.