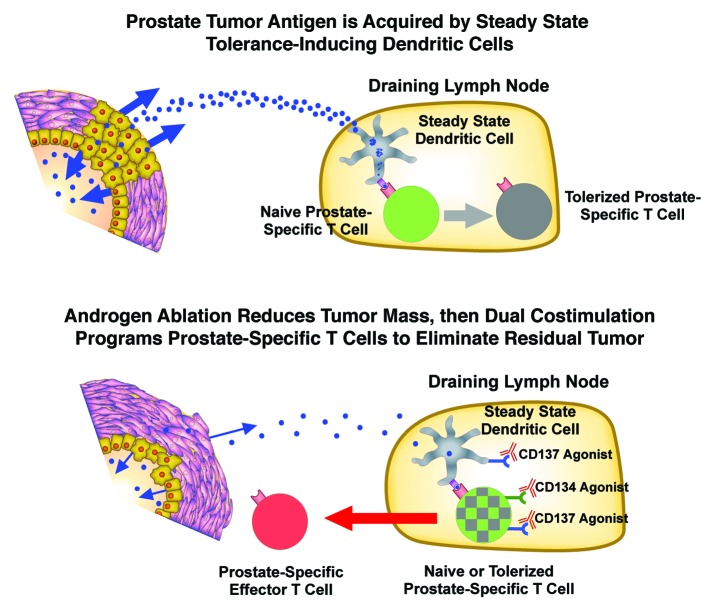
Figure 2. Dual co-stimulation administered following androgen ablation may be an effective combination therapy to treat prostate cancer. Top, prostate tumor antigens presented by steady-state dendritic cells (DCs) in the draining lymph node program prostate-specific T cells to undergo tolerization. Bottom, androgen ablation induces a state of minimal residual disease by causing the majority of tumor cells to undergo cell death. Dual co-stimulation therapy may program prostate-specific T cells to expand, acquire effector functions, and eliminate the residual tumor. Since androgen ablation also induces the regeneration of the aged thymus, these prostate-specific T cells may be naïve recent thymic emigrants (green). Dual co-stimulation may also engage previously tolerized prostate-specific T cells (gray) since CD134 agonists can reverse pre-existing T cell anergy.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.