Figure 1.
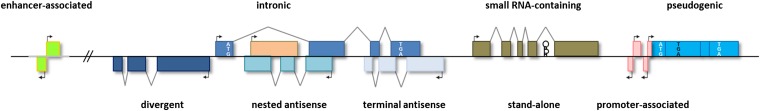
Genomic contexts of lncRNAs. lncRNAs may be stand-alone transcription units, or they may be transcribed from enhancers (eRNAs), promoters (TSSa-RNAs, uaRNAs, pasRNAs, and PROMPTs), or introns of other genes (in this case a protein-coding gene, with start codon ATG and stop codon TGA in white); from pseudogenes (shown here with a premature stop codon TGA in black); or antisense to other genes (NATs) with varying degrees of overlap, from none (divergent), to partial (terminal), to complete (nested). lncRNAs may also host one or more small RNAs (black hairpin) within their transcription units.
