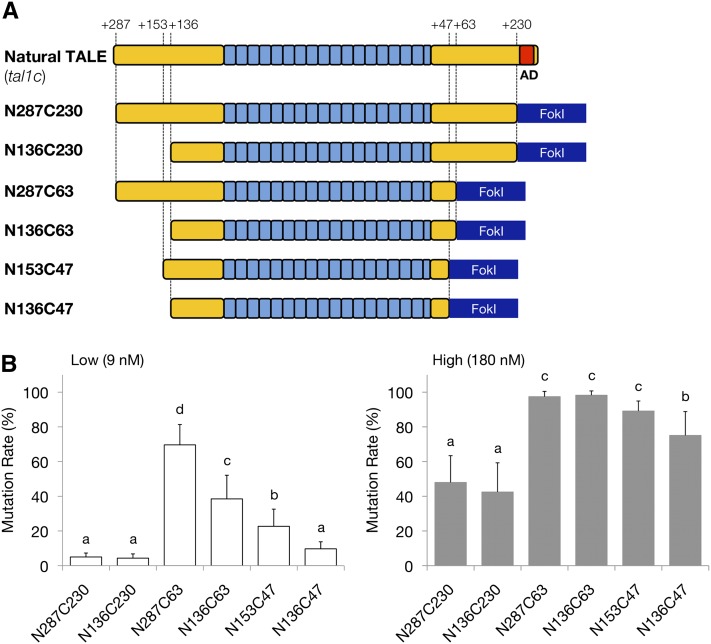
Figure 6.
Effects of the N and C termini of the TAL effector domain on the gene-disrupting activities of deletion variants of DJ1-TALENs. (A) Schematic of deletion variants in the TAL effector domain. A natural TALE (tal1c) has 287 and 278 amino acids in the N- and C-terminal regions of the TAL effector domain, respectively. The transcriptional activation domain (AD) in the C-terminal region is highlighted in red. The names of the deletion variants generated by PCR amplification are indicated on the left side. The numbers of remaining amino acids of the N- and C-terminal regions relative to the position of the repeat modules are shown above. (B) Disruption activities of the truncated TALENs, shown as the mutation rate in the injected embryos. (Left) Mutation rates in the embryos injected with “low” concentrations of RNAs (9 nM) containing a mole ratio equal to 10 ng/µl of RNA for the N136C63 scaffold of the TALENs. (Right) Mutation rates in the embryos injected with “high” concentrations of RNAs (180 nM) containing a mole ratio equal to 200 ng/µl of the N136C63 scaffold. Mutation rate was calculated as the molar concentration of the undigested fragment with HaeIII as a percentage of the sum of the molar concentrations of the undigested fragment and the larger digested fragment. The molar concentration of each fragment was quantified using the MultiNA Viewer software. Columns and error bars represent mean ± SEM (n = 12). The differnt letters at the top of the columns indicate significant differences (P < 0.05; one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s HSD test).