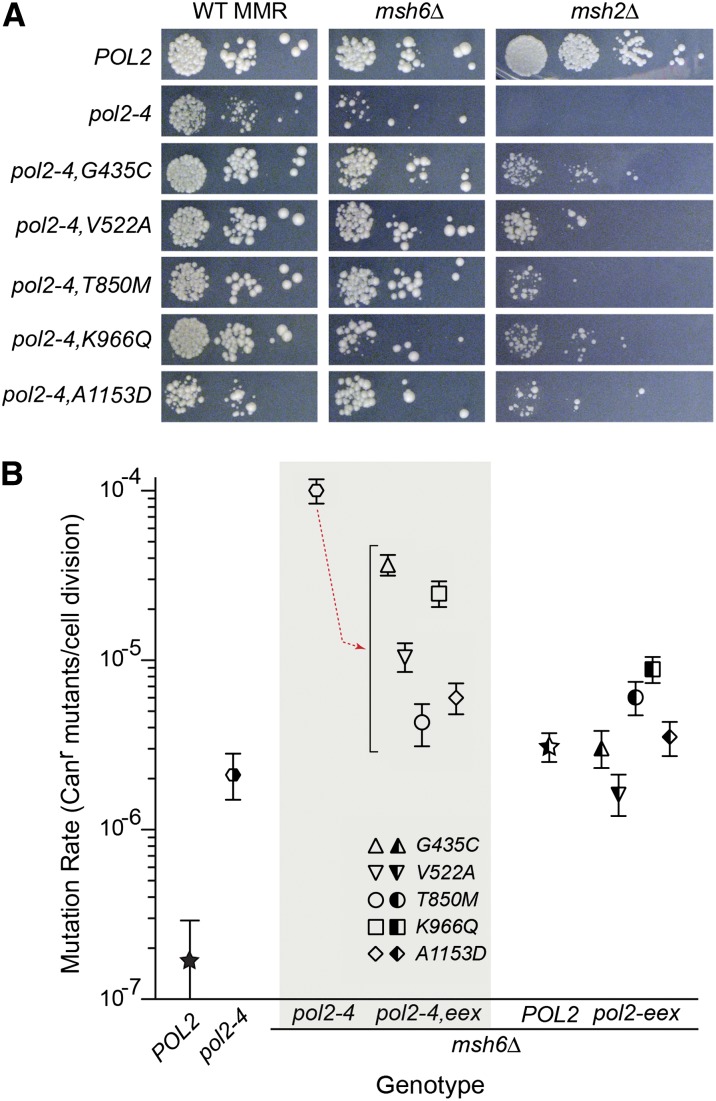
Figure 5.
Growth and antimutator phenotypes conferred by pol2-4 intragenic eex. (A) eex mutations reverse synthetic growth defects associated with pol2-4. The pol2-4,eex mutations were re-engineered into fresh pol2-4–LEU2 plasmids and introduced into wild-type (WT) MMR, msh6Δ, or msh2Δ strains for plasmid shuffling. Strains harboring POL2– or pol2-4–LEU2 plasmids served as controls. Transformants were serially diluted and spotted onto FOA-containing media to assess colony-forming capacity after incubation at 30° for 3 days (WT MMR and msh6Δ) or 4 days (msh2Δ). (B) eex mutations confer antimutator phenotypes. Rates of spontaneous mutation, expressed as Canr mutants/cell division, were determined from multiple independent fluctuation analyses of each strain. Confidence intervals (95%) for each mutation rate are shown as error bars. The downward red arrow in the gray box indicates the antimutator effect of eex alleles on the pol2-4 mutator phenotype. Symbol patterns indicate POL2 and MSH6 allele status: black left half, POL2; black right half, MSH6; solid black, POL2 MSH6; unfilled left half, pol2-4; unfilled right half, msh6Δ; completely unfilled, pol2-4 msh6Δ. Symbol shapes indicate eex allele status (see key insert): star and hexagon, no eex; triangle, G435C; inverted triangle, V522A; circle, T850M; square, K966Q; diamond, A1153D.