Figure 5.
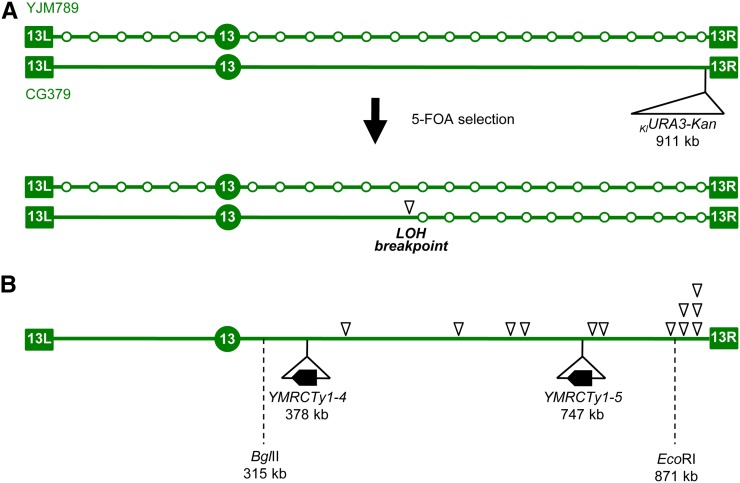
Initial mapping of a candidate fragile site on the right arm of chr13. (A) Experimental rationale. Schematic representation of chr13 in the hybrid diploid strain (JAY800 and JAY801), formed by mating haploids of the diverged strain backgrounds YJM789 and CG379. The open circles in the YJM789-derived chromosome represent SNP positions. The KlURA3-Kan marker was inserted in the CG379-derived chromosome, downstream of the ADH6 gene, near the right telomere. Mitotic crossovers initiated by DNA breaks in the CG379-derived chromosome and repaired using the YJM789 homolog as template result in clones that are resistant to 5-FOA and homozygous for the right end of the YJM789-derived chr13. Genotyping with SNP microarrays can determine the precise site of allelic mitotic recombination (LOH breakpoint, open arrowhead). This site should occur in close proximity to the precursor DNA lesion. (B) LOH breakpoint positions for 12 independent 5-FOA-resistant clones determined by SNP microarray genotyping showing a clustering of breakpoints near the right end of chr13. Also indicated are the relative positions of the two Ty1 elements involved in the chr13/chr5 translocations described in Figures 3 and 4 and the position of the SNP–RFLP markers BglII and EcoRI. The EcoRI marker is described in the Results. The genotype at BglII marker site was also determined and found to be heterozygous in most 5-FOAR clones (117/131; 89.3%).