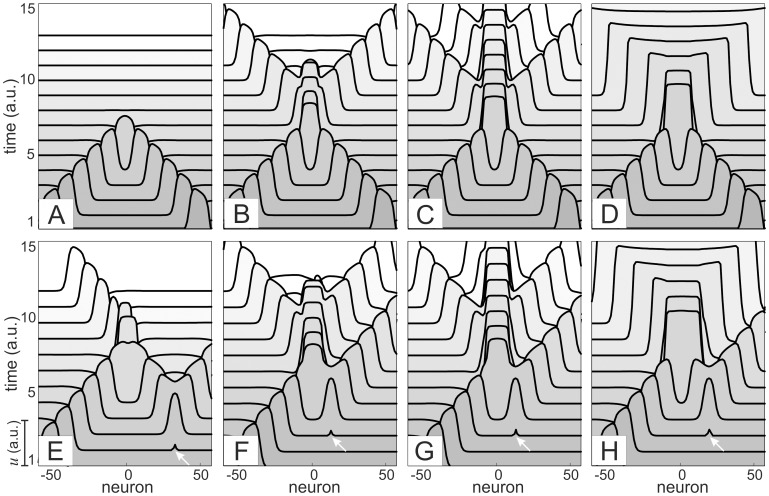
Figure 3. Basic elements of wave-processing of information in the chain of bistable-excitable neurons.
A)–D) Scenarios of symmetric head on collision (central part of the chain is shown). The outcome depends on the magnitude of the additional voltage-dependent membrane current: A) Waves annihilate, 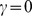 (see also Fig. 2A); B) Waves cross each other,
(see also Fig. 2A); B) Waves cross each other, 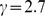 (see also Fig. 2B); C) A pacemaker is formed and emits periodically waves,
(see also Fig. 2B); C) A pacemaker is formed and emits periodically waves, 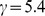 ; and D) Formation of phase switching supersonic waves,
; and D) Formation of phase switching supersonic waves, 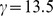 . E)–F) Asymmetric collision of a stationary traveling wave with newly created wave (arrows): E) Only one wave survives after collision,
. E)–F) Asymmetric collision of a stationary traveling wave with newly created wave (arrows): E) Only one wave survives after collision, 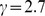 ; F) Two desynchronized waves emerge in collision,
; F) Two desynchronized waves emerge in collision, 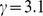 ; G) and H) the same as (C) and (D) but with desynchronization between waves emitted to the left and to the right (
; G) and H) the same as (C) and (D) but with desynchronization between waves emitted to the left and to the right ( ).
).