Table 4. Multivariable logistic regression model for schizophrenia.
| Covariate | Coefficient (SE) | Test Statisticsa | P-valueb | Odds Ratio (95% CI) |
| Intercept | 10.20(2.05) | 24.68 | <0.001 | |
| Gating | 1.00(0.48) | 4.28 | 0.039 | 2.72(1.05–7.00) |
| d’ | −0.37(0.22) | 2.69 | 0.101 | 0.69(0.45–1.07) |
| Arithmetic | −0.32(0.10) | 9.91 | 0.002 | 0.73(0.60–0.89) |
| Block Design | 0.28(0.14) | 3.99 | 0.046 | 1.32(1.01–1.74) |
| Performance IQ | −0.19(0.03) | 13.66 | 0<.001 | 0.90(0.86–0.95) |
| Smoke | 1.58(.80) | 3.88 | 0.049 | 4.87(1.01–23.5) |
SE: standard error; CI: confidence interval.
Gating is defined as a dichotomous variable: P50 gating ratio greater than 0.4 or not.
Smoke is defined as a dichotomous variable: smoking or not.
a Wald chi-square tests.
b P-values were 2-sided.
Multivariable logistic regression model: n = 160, percentage of concordant pairs = 90.4%, percentage of discordant pairs = 9.6%, c statistic = 0.9043, Hosmer-Lemeshow Goodness-of-Fit test p = .640>.05 (df = 8).
The estimated probability of having schizophrenia (the predicted value, 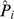 ) can be obtained by using the following formula:
) can be obtained by using the following formula:
where Gating equals 1 if P50 gating ratio >0.4, and 0 otherwise; Smoke equals 1 if smoking, and 0 otherwise.
