Fig. 6.
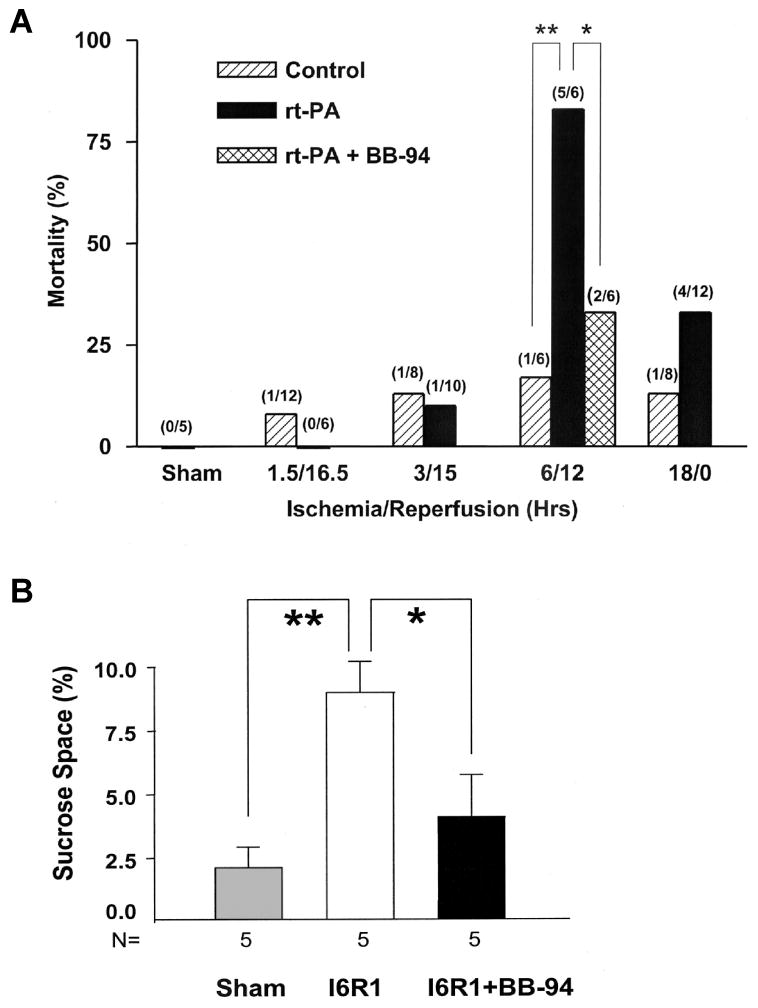
(A) Effect of rtPA on mortality in animals with different intervals of ischemia and reperfusion: Mortality is shown in percent with the numbers of animals dying and the number of animals studied shown in parentheses above the bars. When reperfusion was delayed to 6 hours, mortality was increased markedly in rtPA-treated animals (**P<0.01). Treatment with BB-94 reduced rtPA-associated mortality significantly (*P<0.05). Control animals had MCAO without rtPA treatment. (B) Opening of the BBB as measured by sucrose space in rats with 6 hours of ischemia and 1 hour of reperfusion (I6R1). Compared with sham-operated animals, BBB permeability was markedly increased in untreated rats (**P<0.01). BB-94 given 2 and 5 hours after MCAO markedly decreased BBB opening (*P<0.01). Adapted from Pfefferkorn and Rosenberg, 2003.
