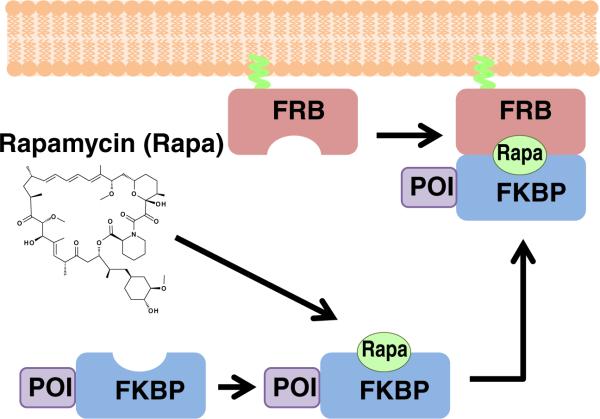
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of a typical CID experiment. Initially, one protein component (in this case, FRB) is anchored at a target site (in this case plasma membrane), while the other protein component (FKBP) is fused to a protein of interest (POI). In the absence of dimerizer, the POI-FKBP fusion protein diffuses freely in the cytoplasm. Upon addition of the dimerizer rapamycin, a ternary complex is formed of FKBP–rapamycin–FRB, which brings the POI to the target site