Figure 3.
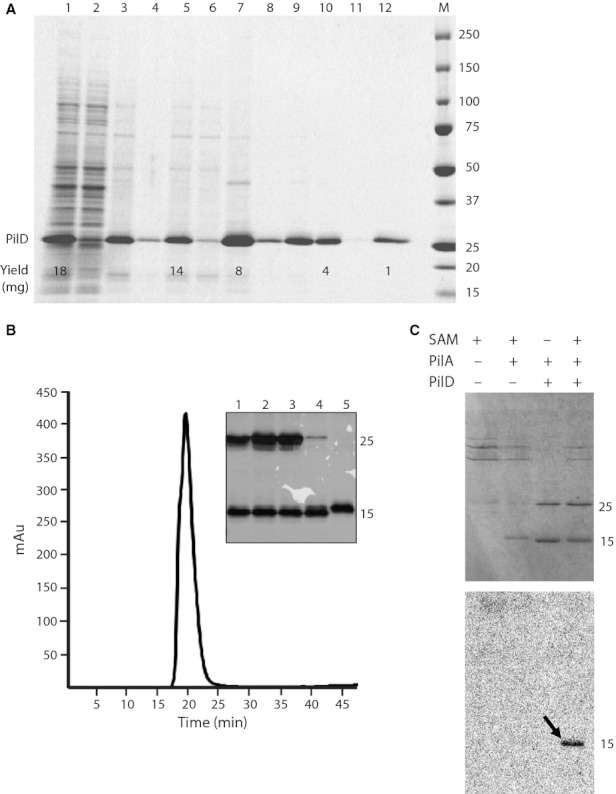
Purification, peptidase, and methyltransferase activities of PilD. (A) Large-scale cell-free synthesis and two-step purification. Lane 1: total translation reaction, 2: translation reaction soluble fraction (not used in purification); 3: total sample after solubilization in 1% dodecyl-β-d-maltoside (DDM); 4: pellet after solubilization; 5: soluble fraction in 1% DDM (applied to immobilized metal-affinity chromatography [IMAC] column); 6: flow-through from IMAC; 7: elution from IMAC; 8: elution fractions concentrated, pellet; 9: elution fractions concentrated, soluble (applied to gel filtration); 10: pooled gel filtration peak fractions; 11: concentrated gel filtration sample, pellet; 12: concentrated gel filtration sample, soluble. Approximate yields are based on tryptophan fluorescence from the PilD band (Kazmin et al. 2002). (B) Gel filtration chromatogram indicates monodispersity of the C-terminally 6x-His-tagged PilD (independent purification from a). Inset: Silver-stained gel showing peptidase activity of PilD. In each case an equal amount of PilA protein (prepared as described in the Experimental Procedures and reclarified by centrifugation at 20,000g for 5 min) was incubated with an equal volume of the indicated PilD sample or buffer. Lane 1: pooled gel filtration peak fractions; 2: peak fractions after concentration; 3: concentrated gel filtration sample, soluble; 4: concentrated gel filtration sample, pellet; and 5: no PilD added. (C) Peptidase and methyltransferase activities of purified PilD. Upper panel: Coomassie stained 15% SDS-PAGE gel. Lower panel: Autoradiograph of the same gel. Lanes are labeled with reaction components. S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) synthetase reaction mixture (high-molecular-weight [MW] bands) serves as the source of freshly synthesized radiolabeled 14C-SAM.
