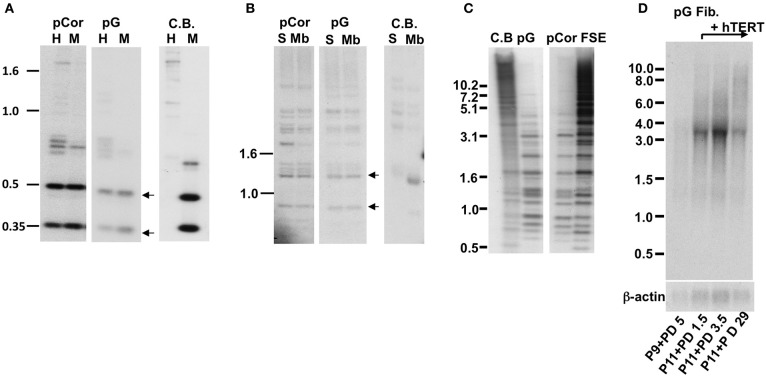
Figure 1.
pG fibroblasts display telomeric abnormalities typical to ICF type I syndrome. (A) Methylation analysis of subtelomeric repeats with NBL-1 probe. DNA samples were digested with either HpaII (H) or MspI (M) restriction enzymes. Blots were hybridized with NBL-1 probe. Arrows point to hybridization bands that appear in HpaII-digested DNA due to hypomethylation of NBL-1 repeats. NBL-1 repeats are heavily methylated in Cord Blood DNA (CB), therefore are not digested with HpaII. (B) Methylation analysis of subtelomeric repeats with Hutel probe. DNA samples were digested with either SauAI (S) or MboI (Mb) restriction enzymes. Blots were hybridized with Hutel probe. Arrows point to hybridization bands that appear in SauAI-digested DNA due to hypomethylation of Hutel repeats. Hutel repeats, which are heavily methylated in cord blood DNA, are not digested with SauAI. (C) Methylation analysis of satellite 2 repeats. Following digestion with BstBI restriction enzyme, DNA was hybridized with a satellite 2 probe. DNA hypomethylated at these repeats is visualized as bands at the lower molecular range, while methylated satellite 2 repeats appear as high molecular bands, as demonstrated with CB and primary fibroblast DNA (FSE). (D) Northern analysis of TERRA expression in pG fibroblasts with and without expression of ectopic hTERT. Northern analysis was carried out with a C-rich (TAACCC)3 probe. Hybridization signals to a β-actin probe on the same blot are shown in the lower panel. The passage (P) and PD at which RNA was extracted from pG fibroblasts, are indicated blow the blots.