Abstract
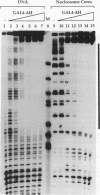
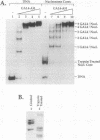
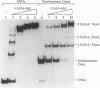
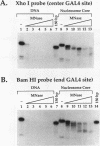
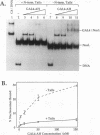
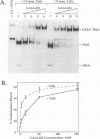
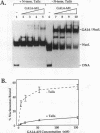
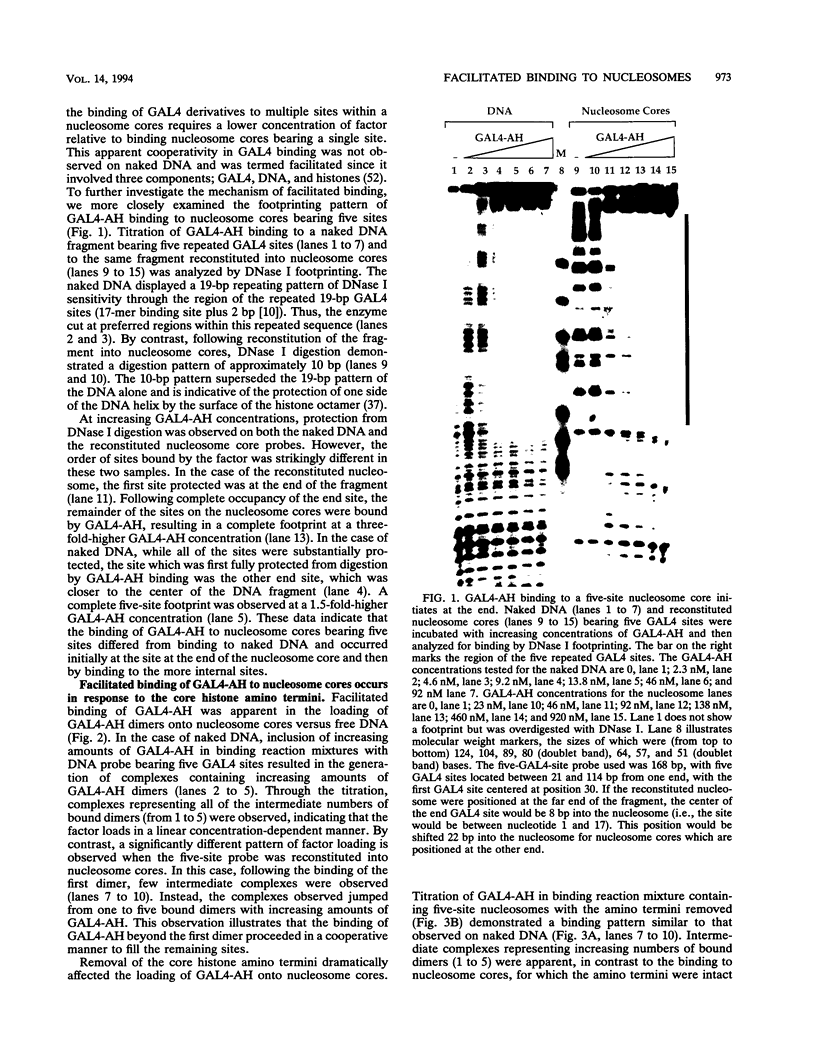
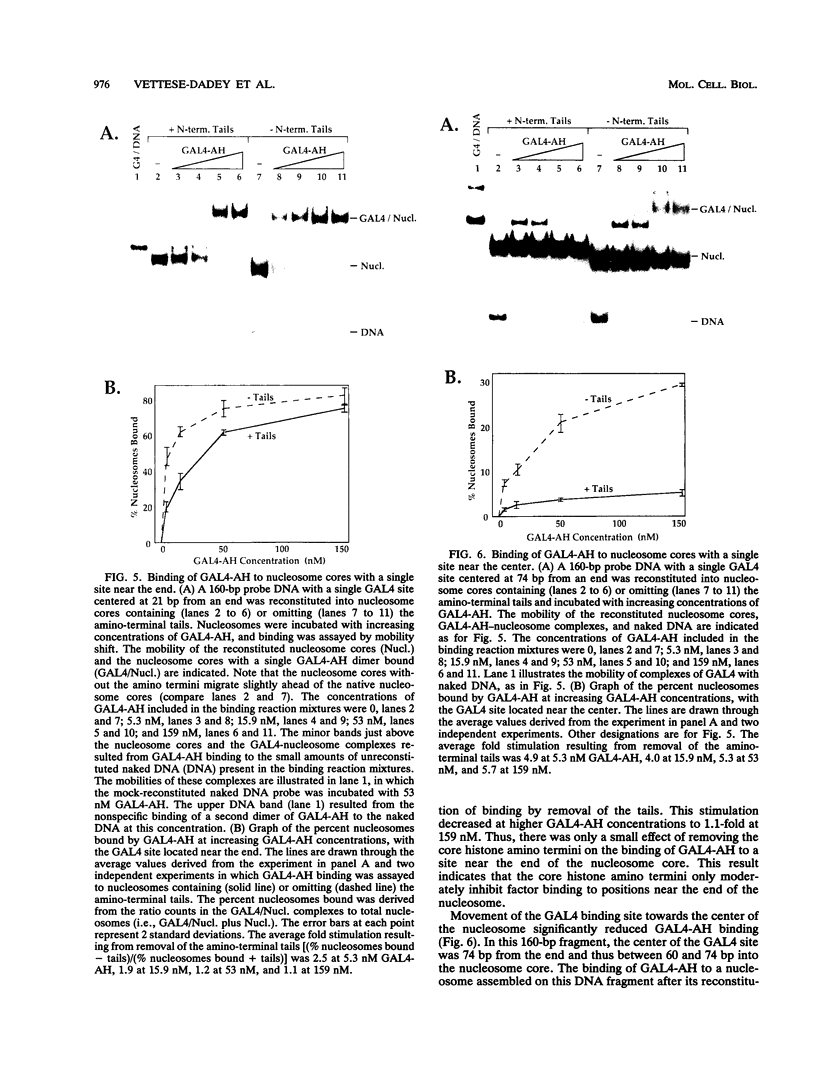
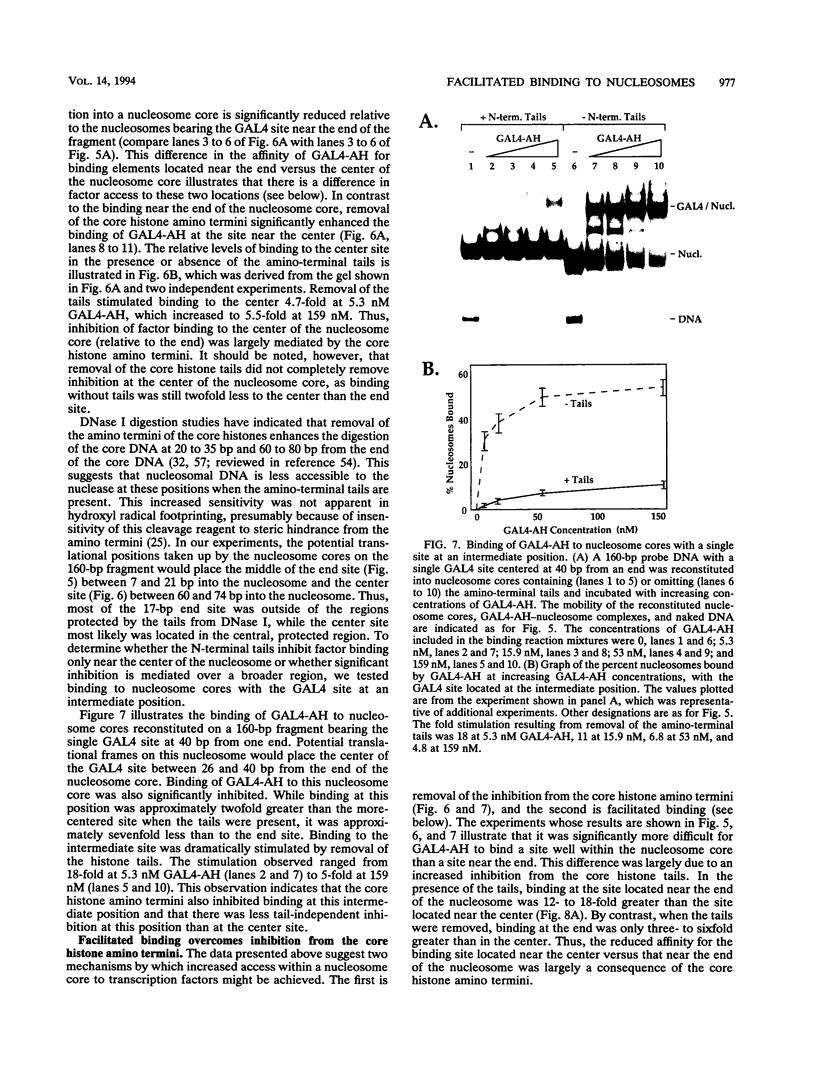
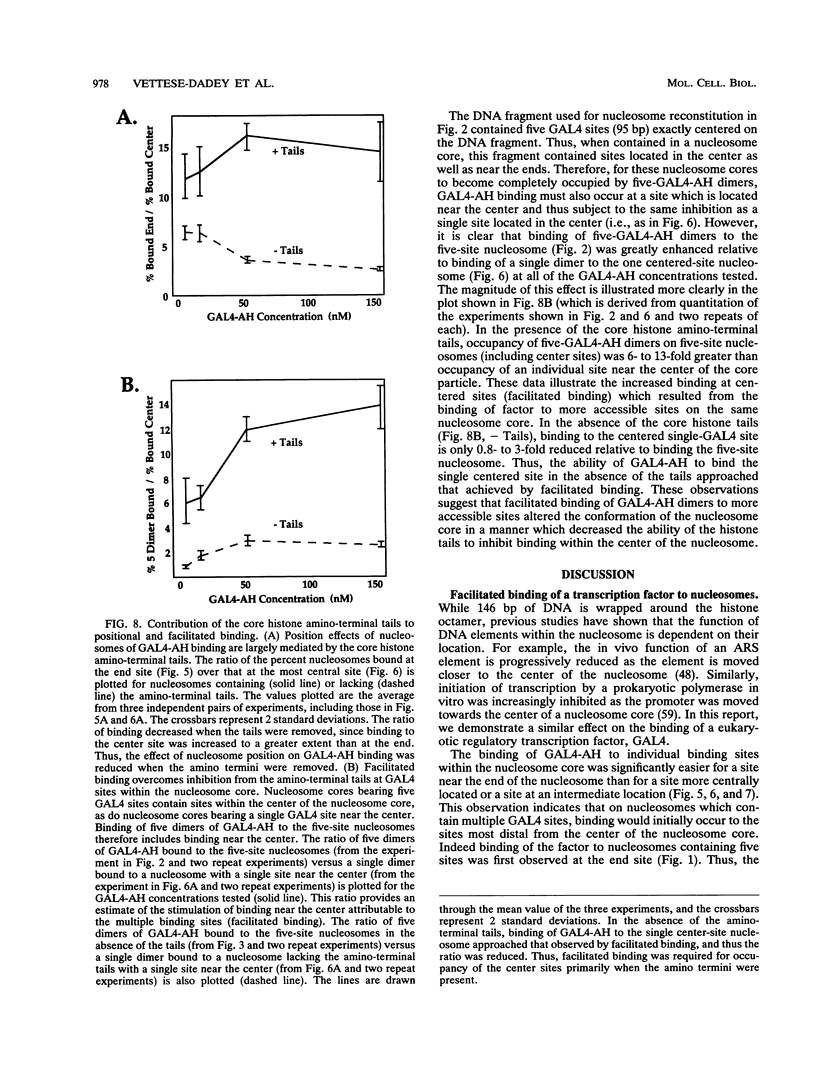
Facilitated, "cooperative" binding of GAL4-AH to nucleosomal DNA occurred in response to inhibition from the core histone amino termini. The binding of GAL4-AH (which contains the DNA-binding and dimerization domains of GAL4) to nucleosome cores containing multiple binding sites initiated at the end of a nucleosome core and proceeded in a cooperative manner until all sites were occupied. However, following tryptic removal of the core histone amino termini, GAL4-AH binding appeared to be noncooperative, similar to binding naked DNA. Binding of GAL4-AH to nucleosomes bearing a single GAL4 site at different positions indicated that inhibition of GAL4 binding was largely mediated by the histone amino termini and primarily occurred at sites well within the core and not near the end. When the histone amino termini were intact, binding of GAL4-AH to sites near the center of a nucleosome core was greatly enhanced by the presence of additional GAL4 dimers bound to more-accessible positions. These data illustrate that the binding of a factor to more-accessible sites, near the end of a nucleosome, allows facilitated binding of additional factors to the center of the nucleosome, thereby overcoming repression from the core histone amino termini. This mechanism may contribute to the binding of multiple factors to complex promoter and enhancer elements in cellular chromatin.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams C. C., Workman J. L. Nucleosome displacement in transcription. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer T. K., Cordingley M. G., Wolford R. G., Hager G. L. Transcription factor access is mediated by accurately positioned nucleosomes on the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):688–698. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., Dong F., van Holde K. E. Use of selectively trypsinized nucleosome core particles to analyze the role of the histone "tails" in the stabilization of the nucleosome. J Mol Biol. 1989 Apr 5;206(3):451–463. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ausio J., van Holde K. E. Histone hyperacetylation: its effects on nucleosome conformation and stability. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 25;25(6):1421–1428. doi: 10.1021/bi00354a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelrod J. D., Reagan M. S., Majors J. GAL4 disrupts a repressing nucleosome during activation of GAL1 transcription in vivo. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):857–869. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Baltimore D. Differentiation requires continuous regulation. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):781–783. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M. How fixed is the differentiated state? Lessons from heterokaryons. Trends Genet. 1989 Aug;5(8):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90100-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. D. The role of stable complexes that repress and activate eucaryotic genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):359–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhm L., Crane-Robinson C. Proteases as structural probes for chromatin: the domain structure of histones. Biosci Rep. 1984 May;4(5):365–386. doi: 10.1007/BF01122502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Kakidani H., Leatherwood J., Mostashari F., Ptashne M. An amino-terminal fragment of GAL4 binds DNA as a dimer. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 5;209(3):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Leatherwood J., Ptashne M. A potent GAL4 derivative activates transcription at a distance in vitro. Science. 1990 Feb 9;247(4943):710–712. doi: 10.1126/science.2405489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey M., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Ptashne M. A mechanism for synergistic activation of a mammalian gene by GAL4 derivatives. Nature. 1990 May 24;345(6273):361–364. doi: 10.1038/345361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. A., Smith M. M., Le S. Y., Sternglanz R., Allfrey V. G. Nucleosome fractionation by mercury affinity chromatography. Contrasting distribution of transcriptionally active DNA sequences and acetylated histones in nucleosome fractions of wild-type yeast cells and cells expressing a histone H3 gene altered to encode a cysteine 110 residue. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6489–6498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croston G. E., Laybourn P. J., Paranjape S. M., Kadonaga J. T. Mechanism of transcriptional antirepression by GAL4-VP16. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2270–2281. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Mann R. K., Grunstein M. Nucleosome loss activates CUP1 and HIS3 promoters to fully induced levels in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;12(4):1621–1629. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.4.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durrin L. K., Mann R. K., Kayne P. S., Grunstein M. Yeast histone H4 N-terminal sequence is required for promoter activation in vivo. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1023–1031. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90554-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S. Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):219–224. doi: 10.1038/355219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour D. S., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Drosophila nuclear proteins bind to regions of alternating C and T residues in gene promoters. Science. 1989 Sep 29;245(4925):1487–1490. doi: 10.1126/science.2781290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunstein M. Histone function in transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:643–678. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.003235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Grunstein M. Nucleosome loss activates yeast downstream promoters in vivo. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):1137–1145. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han M., Kim U. J., Kayne P., Grunstein M. Depletion of histone H4 and nucleosomes activates the PHO5 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2221–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03061.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Clark D. J., Wolffe A. P. Histone contributions to the structure of DNA in the nucleosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6829–6833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong L., Schroth G. P., Matthews H. R., Yau P., Bradbury E. M. Studies of the DNA binding properties of histone H4 amino terminus. Thermal denaturation studies reveal that acetylation markedly reduces the binding constant of the H4 "tail" to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):305–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Curran T. Fos-Jun heterodimers and Jun homodimers bend DNA in opposite orientations: implications for transcription factor cooperativity. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90621-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Zwieb C., Wu C., Adhya S. Bending of DNA by gene-regulatory proteins: construction and use of a DNA bending vector. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Lorch Y. Chromatin structure and transcription. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:563–587. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.003023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Kadonaga J. T. Role of nucleosomal cores and histone H1 in regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II. Science. 1991 Oct 11;254(5029):238–245. doi: 10.1126/science.254.5029.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. Y., Hayes J. J., Pruss D., Wolffe A. P. A positive role for histone acetylation in transcription factor access to nucleosomal DNA. Cell. 1993 Jan 15;72(1):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90051-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M., Tatchell K. Chromatin core particle unfolding induced by tryptic cleavage of histones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Jun;4(6):2039–2055. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.6.2039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Carey M. F., Ptashne M., Green M. R. GAL4 derivatives function alone and synergistically with mammalian activators in vitro. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):659–664. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Initiation on chromatin templates in a yeast RNA polymerase II transcription system. Genes Dev. 1992 Dec;6(12A):2282–2287. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.12a.2282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q., Wallrath L. L., Allan B. D., Glaser R. L., Lis J. T., Elgin S. C. Promoter sequence containing (CT)n.(GA)n repeats is critical for the formation of the DNase I hypersensitive sites in the Drosophila hsp26 gene. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 20;225(4):985–998. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Q., Wallrath L. L., Granok H., Elgin S. C. (CT)n (GA)n repeats and heat shock elements have distinct roles in chromatin structure and transcriptional activation of the Drosophila hsp26 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 May;13(5):2802–2814. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.5.2802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutter L. C. Characterization of DNase-I cleavage sites in the nucleosome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):137–147. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marmorstein R., Carey M., Ptashne M., Harrison S. C. DNA recognition by GAL4: structure of a protein-DNA complex. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):408–414. doi: 10.1038/356408a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meersseman G., Pennings S., Bradbury E. M. Mobile nucleosomes--a general behavior. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2951–2959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondek B., Gloss L., Herr W. The SV40 enhancer contains two distinct levels of organization. Nature. 1988 May 5;333(6168):40–45. doi: 10.1038/333040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T. Glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding specificity is increased by the organization of DNA in nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3884–3888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Wrange O. Specific glucocorticoid receptor binding to DNA reconstituted in a nucleosome. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3073–3079. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03172.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pham T. A., Hwung Y. P., McDonnell D. P., O'Malley B. W. Transactivation functions facilitate the disruption of chromatin structure by estrogen receptor derivatives in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18179–18187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piña B., Brüggemeier U., Beato M. Nucleosome positioning modulates accessibility of regulatory proteins to the mouse mammary tumor virus promoter. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):719–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90087-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Laskey R. A. Assembly of nucleosomes and chromatin in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1989;170:575–585. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)70065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D. Structural analysis of a triple complex between the histone octamer, a Xenopus gene for 5S RNA and transcription factor IIIA. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3473–3482. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild C., Claret F. X., Wahli W., Wolffe A. P. A nucleosome-dependent static loop potentiates estrogen-regulated transcription from the Xenopus vitellogenin B1 promoter in vitro. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):423–433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning can affect the function of a cis-acting DNA element in vivo. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):387–389. doi: 10.1038/343387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning: occurrence, mechanisms, and functional consequences. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:143–184. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60841-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straka C., Hörz W. A functional role for nucleosomes in the repression of a yeast promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):361–368. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07957.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svaren J., Hörz W. Histones, nucleosomes and transcription. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Apr;3(2):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90026-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. C., Workman J. L., Schuetz T. J., Kingston R. E. Facilitated binding of GAL4 and heat shock factor to nucleosomal templates: differential function of DNA-binding domains. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1285–1298. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Protein/DNA architecture of the DNase I hypersensitive region of the Drosophila hsp26 promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2191–2201. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03058.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. M. Histone acetylation and control of gene expression. J Cell Sci. 1991 May;99(Pt 1):13–20. doi: 10.1242/jcs.99.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J., Chen T. A., Sterner R., Berger M., Winston F., Allfrey V. G. Affinity chromatography of mammalian and yeast nucleosomes. Two modes of binding of transcriptionally active mammalian nucleosomes to organomercurial-agarose columns, and contrasting behavior of the active nucleosomes of yeast. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5736–5746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. Assembly and propagation of repressed and depressed chromosomal states. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):705–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90267-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitlock J. P., Jr, Simpson R. T. Localization of the sites along nucleosome DNA which interact with NH2-terminal histone regions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6516–6520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winston F., Carlson M. Yeast SNF/SWI transcriptional activators and the SPT/SIN chromatin connection. Trends Genet. 1992 Nov;8(11):387–391. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90300-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Drew H. R. Initiation of transcription on nucleosomal templates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9817–9821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Abmayr S. M., Cromlish W. A., Roeder R. G. Transcriptional regulation by the immediate early protein of pseudorabies virus during in vitro nucleosome assembly. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Buchman A. R. Multiple functions of nucleosomes and regulatory factors in transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Mar;18(3):90–95. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90160-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Kingston R. E. Nucleosome core displacement in vitro via a metastable transcription factor-nucleosome complex. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1780–1784. doi: 10.1126/science.1465613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Roeder R. G., Kingston R. E. An upstream transcription factor, USF (MLTF), facilitates the formation of preinitiation complexes during in vitro chromatin assembly. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1299–1308. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E., Roeder R. G. Control of class II gene transcription during in vitro nucleosome assembly. Methods Cell Biol. 1991;35:419–447. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60582-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]