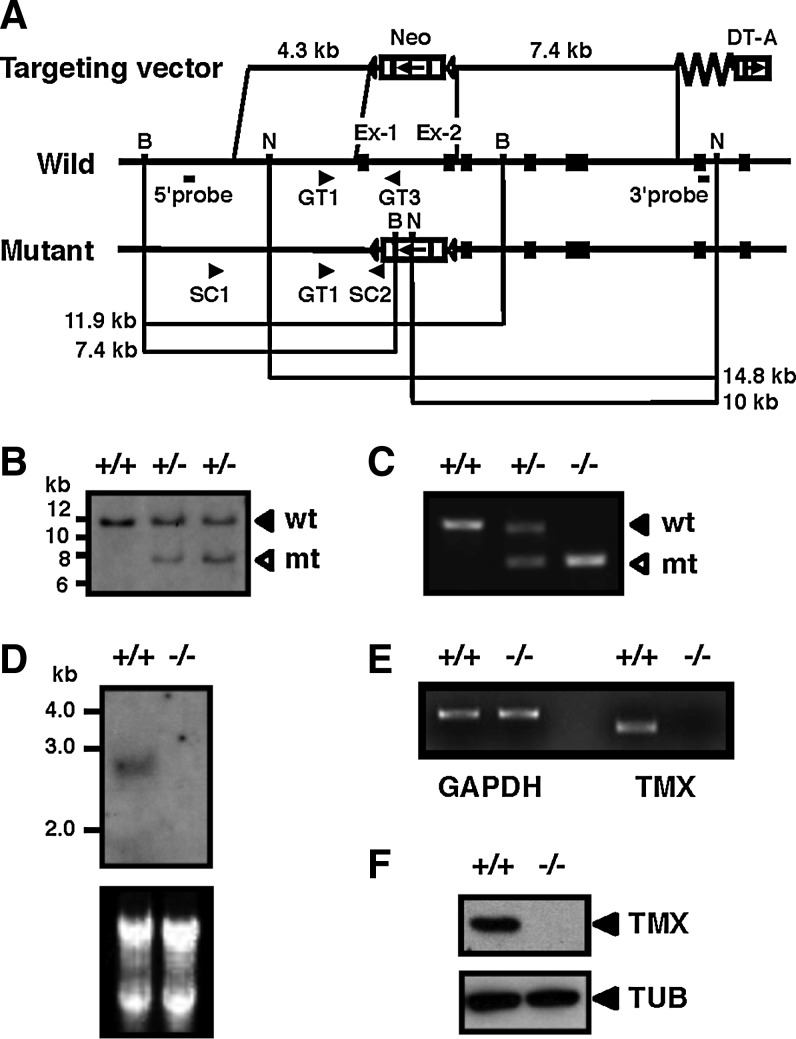
FIG. 1.
Generation of TMX-deficient mice. (A) Structure of the targeting vector (top), the wild-type allele (middle), and the mutant allele (bottom). Exons are represented by filled boxes. The locations of the PCR primers (arrowheads) used for screening of ES cells and genotyping, and the probes for Southern blotting are indicated. (B) Southern blot analysis of BamHI-digested genomic DNA from wild-type (+/+) and targeted (+/−) ES cells using the 5′ probe. wt, wild-type allele; mt, mutant allele. (C) PCR analysis of genomic DNA from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−), and homozygous mice (−/−). (D) Northern blot analysis of TMX. Total RNA from liver tissues with the indicated genotypes was electrophoresed and transferred to a membrane. The blot was hybridized with TMX cDNA as the probe. The ethidium bromide-stained RNA blot is shown in the lower panel. (E) RT-PCR analysis. Total RNA extracted from liver tissues was used to examine the expression of TMX, using glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase as an internal standard. (F) Immunoblot analysis of extracts obtained from whole embryos. Protein samples from wild-type and TMX−/− mice were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies against TMX. α-tubulin (TUB) was used as a loading control. ES, embryonic stem; RT-PCR, reverse transcription–polymerase chain reaction; TMX, transmembrane thioredoxin-related protein.